One-step generation of zebrafish carrying a conditional knockout-knockin visible switch
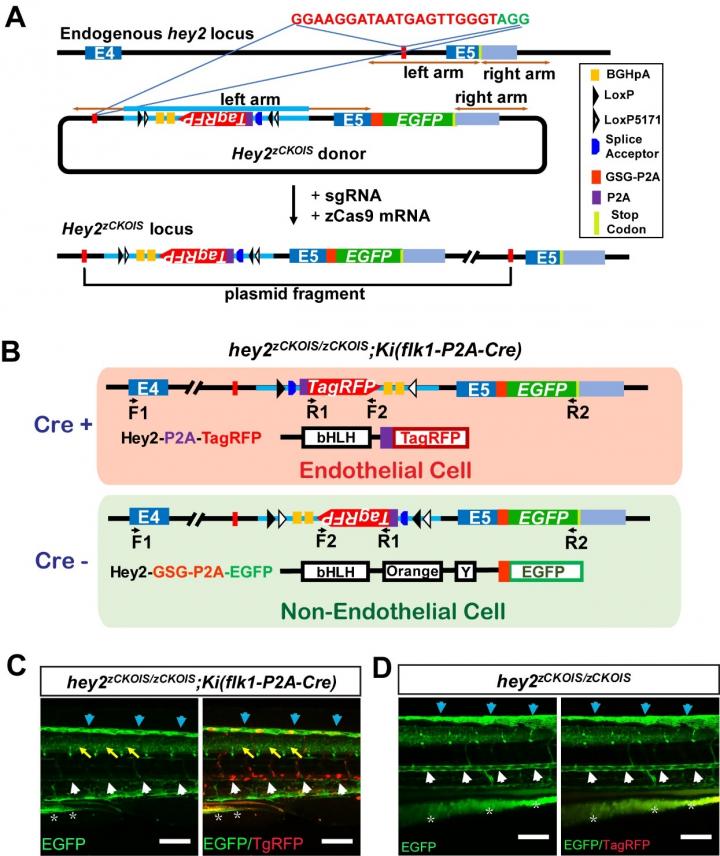
Figure 1A. Schematic of the intron targeting-mediated strategy for generating hey2zCKOIS zebrafish by using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Figure 1B. Schematic of the strategy for endothelial cell (EC)-specific KO of hey2. Figure 1C. Projected confocal images (lateral view) of trunk vessels in a hey2zCKOIS/zCKOIS;Ki(flk1-P2A-Cre) embryos at 3.5 dpf. Figure 1D. In the absent of Cre, EGFP was expressed in the DA (arrowheads), and no red fluorescent signal was not detected in the TagRFP channel. Scale bars, 100 μm. Credit: ©Science China Press
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a vertebrate animal model excellent for in vivo imaging of biological events. However, to knockin two loxP sites in the zebrafish genome is still a big challenge due to the unavailability of gene targeting techniques for zebrafish embryonic stem cells and the low efficiency of homologous recombination (HR) in fast-developing fertilized zebrafish eggs.
Du's lab previously developed a non-HR-mediated efficient KI strategy without destroying targeted genes, in which a Cas9 target is selected in an intron and the donor plasmid is integrated into the targeted intron. This strategy has been used to efficiently make KI zebrafish and mouse.
“We develop a novel method for making zebrafish CKO and KI switch (zCKOIS) in one step based on our previously reported non-HR-mediated intron targeting. We showed that the zCKOIS cassette can be targeted into the last intron of hey2 with a high efficiency via CRIPSR/Cas9 mediated non-HR insertion.” said Dr Jia Li, the co-first author for this work.
A floxed and invertible gene-trap cassette with an RNA slice acceptor is inserted in the intron sequence of the donor plasmid. Without Cre, the zCKOIS cassette will not be inverted and a KI reporter with green fluorescence will be transcripted under the control of the endogenous promoter of the targeted gene.
In the present of Cre, the cassette will be inverse, and the targeted gene will be destroyed, associated with the expression of a KO reporter with red fluorescence. “Using this strategy, we generated a hey2zCKOIS fish line and observed green fluorescence (i.e., KI reporter) in various cell types, including glial cells, endothelial cells (ECs) and haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), similar to the expression pattern of the endogenous hey2 in zebrafish and mouse.” said Dr Jia Li.
By injecting Cre mRNA, they validated that the inverted hey2zCKOIS (hey2zCKOIS-inv) coupled with red fluorescence (i.e., KO reporter) is a non-functional KO allele. Finally, they achieved EC-specific KO of hey2 by crossing the hey2zCKOIS with the KI line Ki(flk1-P2A-Cre), in which Cre expression is driven by the EC-specific promoter flk1.
This method realizes the generation of CKO and KI reporter line in one step via efficient non-HR-mediated insertion. The simplification and combination of CKO and KI make the zCKOIS strategy an applicable approach for zebrafish and even other organisms.
###
This work was supported by grants from the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.31500849), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (18JC1410100, 2018SHZDZX05), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (QYZDY-SSW-SMC028), the Strategic Priority Research Program (XDB32010200) of Chinese Academy of Science, the International Partnership Program, Bureau of International Co-operation of Chinese Academy of Science(153D31KYSB20170059), China Wan-Ren Program, and Shanghai Leading Scientist Program.
See the article: Jia, L., Hongyu, L., Shanye, G, et al. (2019). One-step Generation of Zebrafish Carrying a Conditional Knockout-Knockin Visible Switch via CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Intron Targeting. Sci China Life Sci, in press, https:/
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1607-9All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















