New insight into common cause of blindness
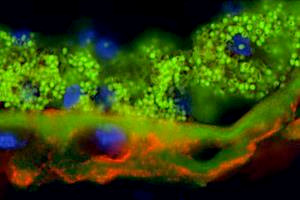
Fluorescent staining of human macula (CFH is red, the FHL-1 protein is green)
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is the major cause of blindness in the western world, affecting around 50 million people. It has been shown that sufferers are genetically predisposed to develop the condition.
One of the most important risk associated genes is called complement factor H (CFH). This encodes a protein called factor H (FH) that is responsible for protecting our eyes from attack by part of our immune system, called the complement system. FH achieves this by sticking to tissues, and when it is present in sufficient quantities it prevents the complement system from causing any damage.
Scientists from the Faculty of Medical and Human Sciences have now discovered that the protein factor H is not the main regulator of immunity in the back of the eye, instead it is a different protein that is made from the same CFH gene. This is called factor H-like protein 1 (FHL-1). The research has been published in the Journal of Immunology.
Dr Simon Clark, a Medical Research Council Career Development Fellow, led the research: “FHL-1 is a smaller version of FH, in fact it is about a third of the size. However, it has all the necessary components to regulate the immune system and is still subject to the genetic alterations that affect AMD risk. Our research has shown that the FHL-1, because it is smaller than FH, can get into structures of the back of the eye which cannot be reached by the larger FH.”
He continues: “Therefore, this research suggests that it is FHL-1 rather than FH which protects the back of the eye from immune attack and that insufficient FHL-1 in the back of the eye may result in inflammation that eventually results in vision loss from AMD. FHL-1, although very similar to FH in many ways, does have a totally unique ‘tail’ structure at its end. This tail seems to mediate how FHL-1 binds tissue. As such, this work has identified a new target for therapeutics aimed at readdressing immune imbalance in the eye, thereby preventing or slowing down AMD.”
Dr Clark successfully identified FHL-1 in human eye tissue that was donated with consent for research following removal of the corneas for transplantation.
He says: “There is no better way to understand and prevent blindness than to use actual human tissue.”
Notes for editors
Media enquiries to:
Jamie Brown
Media Relations Officer
The University of Manchester
Tel: 0161 2758383
Mob: 07887 561318
Email: jamie.brown@manchester.ac.uk
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.manchester.ac.uk/discover/news/article/?id=13283All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















