Cloud Formation: How Feldspar Acts as Ice Nucleus
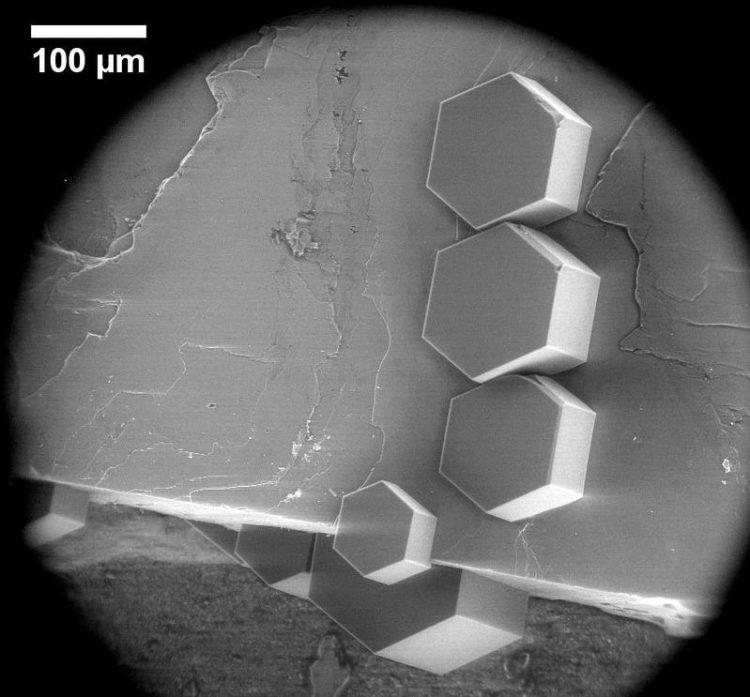
Ice crystals on a feldspar crystallite under the electron microscope. Although they grow on various levels of the feldspar, they have the same orientation. Photo: Alexei Kiselev and Dagmar Gerthsen, KIT
About 90 percent of precipitation over land depends on the formation of ice crystals in clouds, which fall down due to their increasing weight. But water in clouds only freezes when certain particles are present, on which ice crystals can grow. Of all aerosol particles, i.e. solid suspended particles in the atmosphere, however, only few act as ice nuclei.
These rare aerosol particles decisively determine precipitation on earth. Hence, it is important to understand what makes them differ from other particles. “Such an understanding would improve our ability to predict ice and precipitation formation in a future changed climate with changed aerosol loading,” says Professor Thomas Leisner, Head of the Atmospheric Aerosol Research Division of KIT’s Institute of Meteorology and Climate Research (IMK-AAF).
Scientists of IMK-AAF, in cooperation with researchers of the KIT Laboratory of Electron Microscopy (LEM) and University College London (UCL) have now succeeded in solving this question for the most important class of inorganic atmospheric ice nuclei, i.e. mineral dust particles consisting of feldspar.
As is reported in the Science magazine, the scientists combined electron microscopy observations with molecular modeling to determine for the first time the atomic nature of this important inorganic ice nucleus.
They showed that ice starts to grow on feldspar crystallites not on the accessible crystalline faces, but at microscopic defects like edges, cracks, and small depressions. Even though these defects are distributed randomly at the crystallite surface, the ice crystals grow with the same orientation relative to the feldspar crystal lattice.
From these observations and from extensive molecular modeling, the scientists concluded that a specific crystal face that only occurs at defects on the surface of the feldspar crystallite is the underlying nucleus for ice formation.
“Feldspar is one of the most active atmospheric ice nucleating agents, but why it is so good at making ice has remained unclear,” said Professor Angelos Michaelides of UCL. “By identifying the active site for ice nucleation on feldspar, we have found an important piece of the puzzle.” The researchers now expect similar studies to reveal the properties of other minerals acting as ice nuclei.
Alexei Kiselev, Felix Bachmann, Philipp Pedevilla, Stephen J. Cox, Angelos Michaelides, Dagmar Gerthsen, and Thomas Leisner: Active sites in heterogeneous ice nucleation – the example of K-rich feldspars. Science, 2016. DOI: 10.1126/science.aai8034
More about the KIT Climate and Environment Center: http://www.klima-umwelt.kit.edu/english
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
For further information, please contact:
Margarete Lehné
Presse, Kommunikation und Marketing
Phone: +49 721 608-48121
Fax: +49 721 608-45681
margarete.lehne@kit edu
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.kit.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















