Researchers create artificial materials atom-by-atom
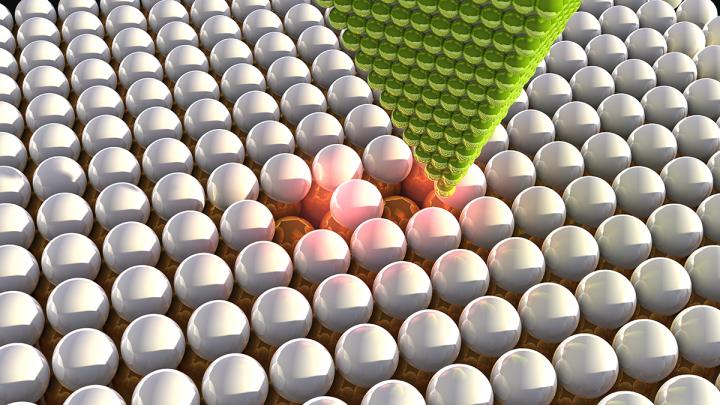
The tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) above chlorine atoms that have been deliberately moved. By moving individual atoms under their microscope, scientists were able to arrange vacancies in a single layer of chlorine atoms and create atomic lattices with a predetermined electrical response. Credit: Ella Maru Studio & Aalto University
Researchers at Aalto University have manufactured artificial materials with engineered electronic properties. By moving individual atoms under their microscope, the scientists were able to create atomic lattices with a predetermined electrical response.
The possibility to precisely arrange the atoms on a sample bring 'designer quantum materials' one step closer to reality. By arranging atoms in a lattice, it becomes possible to engineer the electronic properties of the material through the atomic structure.
Working at a temperature of four degrees Kelvin, the researchers used a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) to arrange vacancies in a single layer of chlorine atoms supported on a copper crystal.
“The correspondence between atomic structure and electronic properties is of course what happens in real materials as well, but here we have complete control over the structure. In principle, we could target any electronic property and implement it experimentally”, says Dr. Robert Drost who carried out the experiments at Aalto University.
Using their atomic assembly method, the research team demonstrated complete control by creating two real-life structures inspired by fundamental model systems with exotic electronic properties.
The approach is not limited to the chlorine system chosen by the research team either. The same method can be applied in many well-understood systems in surface and nanoscience and could even be adapted to mesoscopic systems, such as quantum dots, which are controlled through lithographic processes.
“There are many fascinating theoretical proposals that don't exist in real materials. This is our chance to test these ideas experimentally”, explains Academy Research Fellow Teemu Ojanen at Aalto University.
###
The study was performed at Aalto University's Department of Applied Physics and the groups are parts of the Academy of Finland's Centres of Excellence in Low Temperature Quantum Phenomena and Devices (LTQ) and Computational Nanosciences (COMP). The Aalto Centre for Quantum Engineering (CQE), Academy of Finland and the European Research Council (ERC) funded the research. A consortia funding application to further pursue designer matter is currently under review.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















