A silk coat for diamonds makes sleek new imaging and drug delivery tool
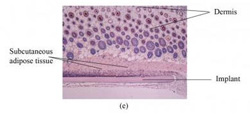
The nanodiamond-silk material, which was implanted into living tissue for two weeks, left no signs of inflammation, suggesting that it's safe for the body.<br><br>Credit: Biomedical Optics Express<br>
The new particles, just tens of nanometers across, are made of diamond and covered in silk. They can be injected into living cells, and because they glow when illuminated with certain kinds of light, biologists can use them to peer inside cells and untangle the molecular circuitry that governs cellular behavior, or to study how cells react to a new drug.
The silk-coated diamond particles could also potentially be used someday in the clinic, by allowing doctors to send infection-fighting antibiotics to a targeted area of the body.
A team of researchers from Australia and the United States describes this new hybrid diamond-silk material in a paper published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Biomedical Optics Express.
Nanodiamonds similar to those in this study have been explored previously for their potential medical uses, but this is the first time silk has been incorporated with nanodiamonds, said Asma Khalid of the University of Melbourne, who is the first author of the Biomedical Optics Express paper. “This nanodiamond-silk hybrid material is important due to the potential it offers to the fields of bioimaging, biosensing and drug delivery,” she explained.
Diamonds are crystals of carbon. But they can be made with defects—other atoms inserted in the crystal structure—and these defects allow them to do tricks that flawless diamonds can't, such as absorbing and reemitting light of certain wavelengths, a process called fluorescence. Because these fluorescent nanodiamonds are bright, stable, and harmless to living tissue – and can work at room temperature – researchers have been exploring their use in biological imaging and sensing. But the edges around the particles tend to be rough and may cause the nanodiamonds to become trapped inside cell membranes.
Previously, other researchers have addressed this problem by coating the particles with lipids, a class of molecules found in fats and waxes. According to the new study, however, a better solution is to cover the nanodiamonds in silk, which is transparent, flexible, compatible with biological tissue, and biodegradable, so it won't leave any harmful byproducts inside the body.
When the researchers tested their new hybrid material, they found that the silk remains transparent, meaning that it does not block the glow of the nanodiamonds. They also discovered that the silk not only preserves the optical properties of the nanodiamonds, but it enhances their brightness by two to four times. Finally, the new material appears to be safe for use in the body: it left no damaging effects even after spending two weeks implanted inside living tissue, suggesting that it is nontoxic and non-inflammatory, the researchers say.
In the future, the team envisions a range of nanodiamond-silk structures that could help researchers improve techniques for fighting infections in targeted areas of the body. A thin film of the new substance, carrying drugs, could be implanted directly into an infected area, minimizing the patient's exposure to the drugs. Silk can also be designed to degrade at a certain rate, which would allow clinicians to control the release of medications.
In addition to the University of Melbourne, the researchers are affiliated with the University of Sydney and the Silk Lab at Tufts University in Massachusetts.
Paper: “Synthesis and Characterization of Biocompatible Nanodiamond-Silk Hybrid Material,” Khalid, A. et al., Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 5, Issue 2, pp. 596-608 (2014).
EDITOR'S NOTE: High-resolution images are available to members of the media upon request. Contact Angela Stark, astark@osa.org.
About Biomedical Optics Express
Biomedical Optics Express is OSA's principal outlet for serving the biomedical optics community with rapid, open-access, peer-reviewed papers related to optics, photonics and imaging in the life sciences. The journal scope encompasses theoretical modeling and simulations, technology development, and biomedical studies and clinical applications. It is published by The Optical Society and edited by Joseph A. Izatt of Duke University. Biomedical Optics Express is an open-access journal and is available at no cost to readers online at http://www.OpticsInfoBase.org/BOE.
About OSA
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional society for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-world applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership programs, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of professionals in optics and photonics.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.osa.orgAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















