Transparent color tunable OLED
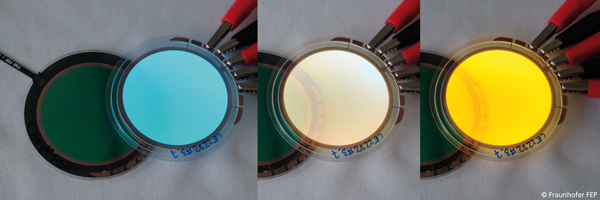
2-color variable transparent OLED module with activated blue, blue and yellow as well as yellow unit © Fraunhofer FEP | Picture in printable resolution: www.fep.fraunhofer.de/press
The objective of the joint project was the development and integration of large-area color variable OLED modules, whereby the light colors red, green and blue (RGB), which are required for the achievement of white mixed light, can be controlled separately.
Thus it is possible to generate any desired color, including white, with one and the same OLED module. The realization of large-area 3-color-variable OLED modules could be demonstrated in the project.
The OLED modules have a diameter of 55 mm with an active light area of 42 mm. They were encapsulated with a full thin film, which enables the lamination of OLED modules in glass composites.
For the first time worldwide a transparent 2-color variable OLED, which can show a color gradient from blue to white to yellow, will be demonstrated. This exhibit will be presented to the visitors of LOPEC 2015 at the Fraunhofer FEP booth.
A possible field of application could be its use as the light source in a laminated glass sheet which serves as baggage compartment in trains. The company SBF Spezialleuchten GmbH, the coordinator of the project, is working on such solutions.
“The possibilities for application of the results, which are achieved within the project, are extraordinarily versatile”, says project manager Jan Hesse. “In addition to the use in general lighting, e.g. in windows, wall elements or wallpapers, the color variable OLEDs are as well suitable for the interior vehicle lighting – especially for the ambient or accent lighting – in the automotive and rail vehicle industry.”
Besides, the aviation industry shows great interest in using this technology for ambient lighting within an aircraft cabin.
The results which were achieved in the project LOIGB provide a basis for further activities at Fraunhofer FEP. Currently, the scientists are working on the process development in order to achieve higher yield and reduce manufacturing costs as well as to realize the process transfer to a roll-to-roll system for flexible OLED. Moreover, the intuitive control of such lighting elements will become a priority. Compared to conventional light sources (on / off), the complex functionality (dimmability, color variation and dynamization through segments) requires new intuitive control possibilities. A simple control is absolutely necessary in order to achieve market acceptance for that innovative lighting technology.
The visitors of LOPEC 2015 are invited to inform themselves about recent developments of our institute in the field of organic semiconductors through the following lectures and poster:
• Dr. Olaf Hild:
“Development of OLED-microdisplay with µ-structured R,G,B subpixels”,
Session Devices I: OLED; March 4th 2015, 11.50 a.m.
• Susan Mühl:
“Adjustable nanowire anisotropy of slot die coated anode layers and its influence to OLED performance”; March 4th 2015, 03.00 p.m.
• Claudia Keibler:
“ALD-film: flexibility versus barrier function”
Poster session on March 4th 2015, 06.00 – 08.00 p.m.
The project was funded by the European Union and the Free State of Saxony.
Funding reference: 100133280
Press contact:
Annett Arnold
Fraunhofer Institute for Organic Electronics, Electron Beam and Plasma Technology FEP| Phone +49 351 2586 452 | Annett.Arnold@fep.fraunhofer.de
Winterbergstraße 28 | 01277 Dresden | Germany | www.fep.fraunhofer.de
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Trade Fair News
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















