Future of LEDs gets boost from verification of localization states in InGaN quantum wells
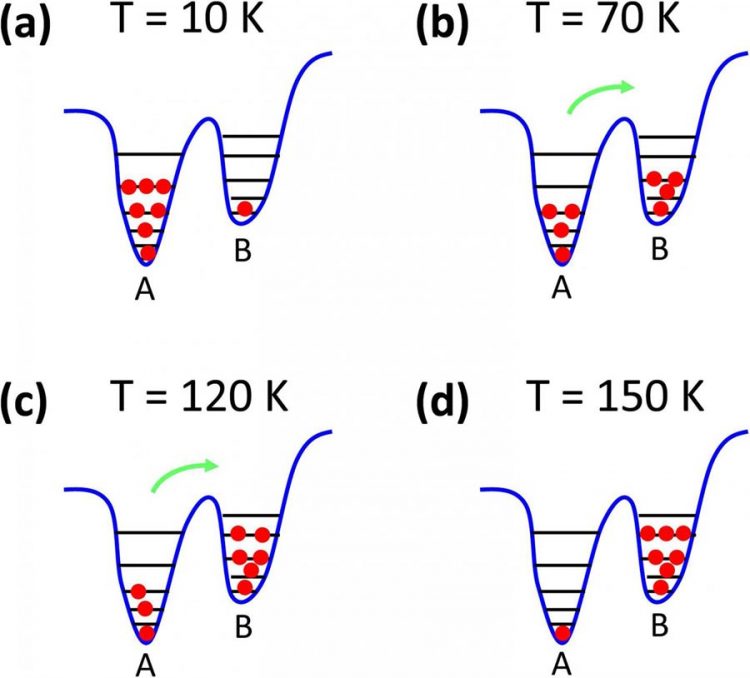
LEDs made of indium gallium nitride provide better luminescence efficiency than many of the other materials used to create blue and green LEDs, but a big challenge of working with InGaN is its known dislocation density defects that make it difficult to understand its emission properties. Researchers report an InGaN LED structure with high luminescence efficiency and what is believed to be the first direct observation of transition carriers between different localization states within InGaN. This figure shows the transition process of carriers between different localization states with increasing temperatures. Credit: Yangfeng Li Usage Restrictions: Journalists may use this image only with appropriate credit.
Light-emitting diodes made of indium gallium nitride provide better luminescence efficiency than many of the other materials used to create blue and green LEDs. But a big challenge of working with InGaN is its known dislocation density defects that make it difficult to understand its emission properties.
In the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, researchers in China report an InGaN LED structure with high luminescence efficiency and what is believed to be the first direct observation of transition carriers between different localization states within InGaN. The localization states were confirmed by temperature-dependent photoluminescence and excitation power-dependent photoluminescence.
Localization states theory is commonly used to explain the high luminescence efficiency gained via the large number of dislocations within InGaN materials. Localization states are the energy minima states believed to exist within the InGaN quantum well region (discrete energy values), but a direct observation of localization states was elusive until now.
“Based primarily on indium content fluctuations, we explored the 'energy minima' that remain within the InGaN quantum well region,” said Yangfeng Li, the paper's lead author and a now postdoctoral fellow at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. “Such energy minima will capture the charge carriers — electrons and holes — and prevent them from being captured by defects (dislocations). This means that the emission efficiency is less affected by the large number of defects.”
The group's direct observation of localization states is an important discovery for the future of LEDs, because it verifies their existence, which was a long-standing open scientific question.
“Segregation of indium may be one of the reasons causing localization states,” said Li. “Due to the existence of localization states, the charge carriers will mainly be captured in the localization states rather than by nonradiative recombination defects. This improves the high luminescence efficiency of light-emitting devices.”
Based on the group's electroluminescence spectra, “the InGaN sample with stronger localization states provides more than a twofold enhancement of the light-output at the same current-injection conditions as samples of weaker localization states,” Li said.
The researchers' work can serve as a reference about the emission properties of InGaN materials for use in manufacturing LEDs and laser diodes.
They plan to continue to explore gallium nitride-related materials and devices “not only to gain a better understanding of their localizations but also the properties of InGaN quantum dots, which are semiconductor particles with potential applications in solar cells and electronics,” Li said. “We hope that other researchers will also conduct in-depth theoretical studies of localization states.”
###
The article, “Visualizing carrier transitions between localization states in a InGaN yellow-green light-emitting-diode structure,” is authored by Yangfeng Li, Zhen Deng, Ziguang Ma, Lu Wang, Haiqiang Jia, Wenxin Wang, Yang Jiang and Hong Chen. The article appears in the Journal of Applied Physics (DOI: 10.1063/1.5100989) and can be accessed at http://aip.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.5100989All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















