Fermilab successfully demonstrates new technique to improve particle beams
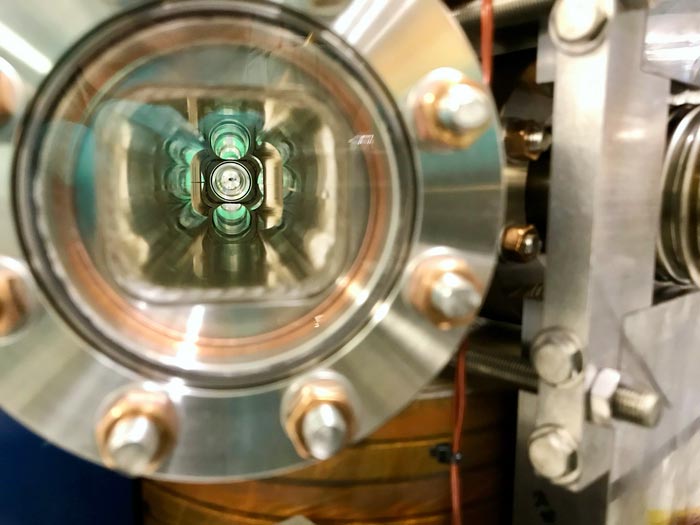
A view looking downstream through the beam pipe of the IOTA ring. The optical stochastic cooling experiment occupies one of the straight sections of the IOTA ring and cools the stored beam, similar to the way radio-frequency stochastic cooling cooled antiprotons in the Recycler during the Tevatron era.
Credit: Jamie Santucci, Fermilab
Physicists love to smash particles together and study the resulting chaos. Therein lies the discovery of new particles and strange physics, generated for tiny fractions of a second and recreating conditions often not seen in our universe for billions of years. But for the magic to happen, two beams of particles must first collide.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory have announced the first successful demonstration of a new technique that improves particle beams. This demonstration could be used in future particle accelerators to potentially use the method to create better, denser particle beams, increasing the number of collisions and giving researchers a better chance to explore rare physics phenomena that help us understand our universe. The team published its findings in a recent edition of Nature.
At Fermilab, scientists used the lab’s newest storage ring, the Integrable Optics Test Accelerator, known as IOTA, to demonstrate and explore a new kind of beam cooling technology with the potential to dramatically speed up that cooling process.
The new technique is called optical stochastic cooling and this cooling system measures how particles in a beam move away from their ideal course using a special configuration of magnets, lenses and other optics to give corrective nudges.
“It’s exciting because this is the first cooling technique demonstrated in the optical regime, and this experiment let us study the most the essential physics of the cooling process,” Jarvis said. “We’ve already learned a lot, and now we can add another layer to the experiment that brings us significantly closer to real applications.”
With the initial experiment completed, the science team is developing an improved system at IOTA that will be the key to advancing the technology. It will use an optical amplifier to strengthen the light from each particle by about a factor of 1,000 and apply machine learning to add flexibility to the system.
“Ultimately, we’ll explore a variety of ways to apply this new technique in particle colliders and beyond,” Jarvis said. “We think it’s very cool.”
Read the full story about IOTA’s recent result: First demonstration of a new particle beam technology at Fermilab
Research at IOTA is supported by the DOE Office of Science.
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory is America’s premier national laboratory for particle physics research. A U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science laboratory, Fermilab is located near Chicago, Illinois, and operated under contract by the Fermi Research Alliance LLC. Visit Fermilab’s website at https://www.fnal.gov/ and follow us on Twitter @Fermilab.
Media Contact
Tracy Marc
DOE/Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory
tracym@fnal.gov
Office: 224-290-7803
Original Source
https://news.fnal.gov/2022/08/first-demonstration-of-a-new-particle-beam-technology-at-fermilab/
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















