Latest News
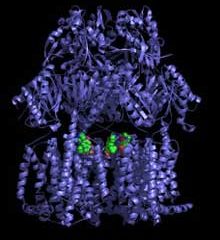
Secrets Of Drug Resistance Revealed
In the race to stay one step ahead of drug-resistant bacteria, scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the University of California at Berkeley obtained high-resolution images of a protein complex found in bacteria that repels a wide range of antibiotics.
The images, which appear in the May 9 issue of Science, offer new insight into how bacteria survive attacks from different antibiotics, a growing health problem called multidrug resistance. As the team learned, these robu

Infineon and Micron announce RLDRAM II Specification
Next-Generation, High-bandwidth Memory Architecture Targets Communication Data Storage Applications
Infineon Technologies AG and Micron Technology, Inc., today announced the release of the complete specification for reduced latency DRAM II (RLDRAM™ II) architecture. Operating at speeds of up to 400 MHz, RLDRAM II products are the second-generation, ultra high-speed double data rate (DDR) SDRAM that combines fast random access with extremely high bandwidth and high density targeting co

"Talking windscreens" could help prevent accidents
Drivers are four times more likely to have an accident if they use a mobile phone on the road. However, using a “talking windscreen” rather than a traditional mobile phone while driving could reduce this risk, and so help to prevent accidents, according to Oxford University research just published in Psychological Science.
A growing body of evidence shows that using a hands-free phone is as problematic for drivers as using a hand-held phone. It is probably the distraction of a driver´s atte

New Jersey Institute of Technology physicist uncovers new information about plutonium
The storage of plutonium has long plagued scientists. “It is a dangerous metal and its long term storage must be done with special care so as not to harm the environment, ”said physicist Serguei Savrasov, Ph.D.
Finding a solution to this problem led Savrasov, an associate professor at New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT), and a team of researchers at Rutgers University and Los Alamos National Laboratories, to study how this metal reacts to heat, a natural condition of storage over time

Clue to prion formation found, offers step toward treating puzzling diseases
Prions—their existence is intriguing and their links to disease are unsettling. These unconventional infectious agents are involved in mad cow disease and other fatal brain illnesses in humans and animals, rattling prior assumptions about the spread of infections.
Dartmouth Medical School biochemists studying the mysteries of these prion particles have discovered a novel step in their formation. Their results, reported in a recent issue of Biochemistry could help provide a new approach for

Greenhouse gas might green up the desert
Weizmann Institute study suggests that rising carbon dioxide levels might cause forests to spread into dry environments
Missing: around 7 billion tons of carbon dioxide (CO2), the main greenhouse gas charged with global warming. Every year, industry releases about 22 billion tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. And every year, when scientists measure the rise of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, it doesn’t add up – about half goes missing. Figuring in the amount that could be s