Latest News

Distinctive Genetic Program Guides Breast Cancer’s Deadly Spread
Researchers have peered inside breast cancer’s toolbox and identified a set of rogue genes that accelerates the spread of cancer from its primary site in the breast to a secondary location in bone marrow. The genes identified by the scientists are distinct from those that spawn the initial tumor, which invites speculation about whether different cancers bear unique “gene expression signatures” that increase the probability that a cancer will spread in a process called metastasis.
Metast

The EU joins forces with international partners on research to "clean up" fossil fuels
Today in Washington the European Commission, represented by Loyola de Palacio, Vice President in charge of Energy and Transport, signed an international charter on CO2 capture and storage (CO2/carbon sequestration).
This will create the “Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum” with Australia, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Italy, India, Japan, Mexico, Norway, the People’s Republic of China, Russia, the United Kingdom and the US. The Forum aims to stimulate research into carbon sequestratio

Purdue genetic discovery may aid plants and human medicine
Findings that two mutated genes alter plant growth and development could result in improved plants and enhanced cancer treatments, according to Purdue University researchers.
In a paper published in Thursday’s (6/26) issue of Nature, the scientists report that these abnormal, or mutant plants are able to reorient themselves in response to light and gravity more rapidly than normal, or “wild type,” plants. Apparently plants behave differently in accordance with how a growth hormon
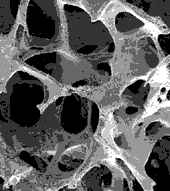
Tissue Engineered Bone Grows Strong
By closely following nature’s blueprint, Toronto researchers have developed an innovative way to speed the healing of severe bone breaks, resulting in what may be the thickest tissue-engineered bone ever produced in the laboratory.
The new bone grows naturally without the addition of chemical growth stimulants, said Whitaker investigator Molly Shoichet, Ph.D., of the University of Toronto. The innovation is in the design of the synthetic scaffold that provides a framework for the growin

UT Southwestern researchers pinpoint role cell surface protein group plays in brain function
A specific group of brain proteins is essential to activate communication between neurons, and without this group of proteins all functions of the central nervous system are disrupted, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas have discovered.
The disruption of this specialized group of proteins, called alpha-Neurexins, causes severe interruption of synaptic transmission, which is essential for neurons to communicate in the central nervous system. Synapses are specialized junc

For ferrets, GPI means ’get pregnancy initiated’
Embryo-implant protein exploited by tumors may help endangered species
Knowing what makes a ferret pregnancy take hold could help biologists save endangered species or understand how tumors spread.
Specifically, biologists examining early pregnancy in domestic ferrets report they have identified a protein necessary for embryos to implant successfully in the wall of the uterus, which is pregnancy’s first step in mammals.
Newly discovered as a molecular signal i