Latest News

Behavior of arctic ocean ridge confounds predictions; May lead to new insights into crust formation
The discovery that an ocean ridge under the Arctic ice cap is unexpectedly volcanically active and contains multiple hydrothermal vents may cause scientists to modify a decades-long understanding of how ocean ridges work to produce the Earth’s crust.
The new results, which come from a study of the Gakkel Ridge, one of the slowest spreading ridges on Earth, have broad implications for the understanding of the globe-encircling mid-ocean ridge system where melting of the underlying mantle
Scientists announce first 3-D assembly of magnetic and semiconducting nanoparticles
Scientists from Columbia University, IBM and the University of New Orleans today announced a new, three-dimensional designer material assembled from two different types of particles only billionths of a meter across.
In the June 26 issue of the journal Nature, the team describes the precision chemistry methods developed to tune the particles’ sizes in increments of less than one nanometer and to tailor the experimental conditions so the particles would assemble themselves into repeating 3-

Astronomers find Paschen in the bar
An international team of astronomers have used a unique instrument on the 8-m Gemini South Telescope to determine the ages of stars across the central region of the barred spiral galaxy, M83. Preliminary results provide the first hints of a domino model of star formation where star formation occurs in a time sequence, driven by the movements of gas and stars in the central bar.
The new instrument, called CIRPASS, simultaneously produces 500 spectra, taken from across the whole region of inte
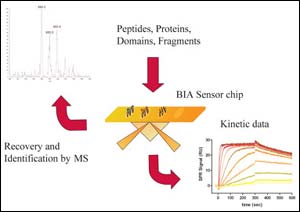
Biochips in Drug Development
Biomolecular interaction analysis (BIA) using SPR (surface plasmon resonance) biosensors is now utilised increasingly in nearly all phases of drug development. The BIA system consists out of a light source emitting near infrared light, a sensor microchip, an automated liquid handling system with constant flow and a diode array position-sensitive detector. One of the two interacting partners (referred to as the ligand) is immobilized on the sensor surface. The other binding partner, called the analy

First Direct Evidence Of Fullerenes In Meteorite Samples
The first direct evidence of fullerenes in material originating from outer space could reinforce the meteorite impact theory of mass extinction on Earth and the existence of fullerenes in interstellar dust. The existence, or not, of the closed-cage carbon molecules known as fullerenes in outer space has been an area of controversy. A team from Reading University in the UK is publishing its findings in Proceedings A, a Royal Society scientific journal.
Allende meteorite
The me
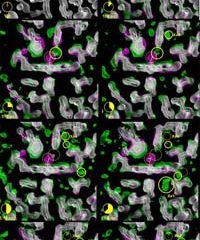
Filming an ultra-fast biological reaction essential to life
A team of scientists from the USA in collaboration with staff at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (Schotte et al) have managed to film a protein at work in unprecedented detail. The protein is the oxygen-storing molecule myoglobin, which plays a central role in the production of energy in muscles. The motion of the protein was recorded using ultra-short flashes of X-ray light from the synchrotron. The new insight in the functionality of myoglobin has led to a deeper understanding of the m