Your next wooden chair could arrive flat, then dry into a 3D shape
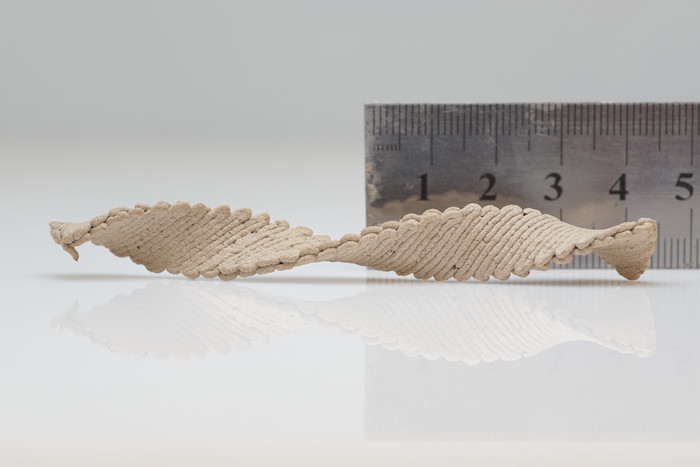
Wood ink printed as a flat rectangle is programmed to form a complex shape after drying and solidifying. (Ruler is marked in centimeters.)
Credit: Doron Kam
Wooden objects are usually made by sawing, carving, bending or pressing. That’s so old school! Today, scientists will describe how flat wooden shapes extruded by a 3D printer can be programmed to self-morph into complex 3D shapes. In the future, this technique could be used to make furniture or other wooden products that could be shipped flat to a destination and then dried to form the desired final shape.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2022 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person Aug. 21–25, with on-demand access available Aug. 26–Sept. 9. The meeting features nearly 11,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
A video on the research is available at www.acs.org/printingwood.
In nature, plants and some animals can alter their own shapes or textures. Even after a tree is cut down, its wood can change shape as it dries. It shrinks unevenly and warps because of variations in fiber orientation within the wood. “Warping can be an obstacle,” says Doron Kam, a graduate student who is presenting the work at the meeting, “but we thought we could try to understand this phenomenon and harness it into a desirable morphing.”
Unlike some natural objects, artificial structures can’t typically shape themselves, says Eran Sharon, Ph.D., one of the project’s principal investigators. But scientists in recent years have begun printing flat sheets that could form themselves into 3D shapes after a stimulus, such as a change in temperature, pH or moisture content, says Sharon. However, these self-morphing sheets were made from synthetic materials, such as gels and elastomers, he notes.
“We wanted to go back to the origin of this concept, to nature, and do it with wood,” says Sharon. He and Kam — as well as Shlomo Magdassi, Ph.D., and Oded Shoseyov, Ph.D., the other principal investigators who took on this challenge with Ido Levin, Ph.D., who was a graduate student at the time — are at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
A few years ago, the team developed an environmentally friendly water-based ink composed of wood-waste microparticles known as “wood flour” mixed with cellulose nanocrystals and xyloglucan, which are natural binders extracted from plants. The researchers then began using the ink in a 3D printer. They recently discovered that the way the ink is laid down, or the “pathway,” dictates the morphing behavior as the moisture content evaporates from the printed piece. For instance, a flat disk printed as a series of concentric circles dries and shrinks to form a saddle-like structure reminiscent of a Pringles® potato chip, and a disk printed as a series of rays emanating from a central point turns into a dome or cone-like structure.
The ultimate shape of the object can also be controlled by adjusting print speed, the team found. That’s because shrinkage occurs perpendicular to the wood fibers in the ink, and print speed changes the degree of alignment of those fibers. A slower rate leaves the particles more randomly oriented, so shrinkage occurs in all directions. Faster printing aligns the fibers with one another, so shrinkage is more directional.
The scientists learned how to program the print speed and pathway to achieve a variety of final shapes. They found that stacking two rectangular layers that are printed in different orientations yields a helix after drying. In their latest work, they found that they can program the printing pathway, speed and stacking to control the specific direction of shape change, such as whether rectangles twist into a helix that spirals clockwise or counterclockwise.
Further refinement will allow the team to combine the saddles, domes, helices and other design motifs to produce objects with complicated final shapes, such as a chair. Ultimately, it could be possible to make wood products that are shipped flat to the end user, which could reduce shipping volume and costs, Kam says. “Then, at the destination, the object could warp into the structure you want.” Eventually, it might be feasible to license the technology for home use so consumers could design and print their own wooden objects with a regular 3D printer, Sharon says.
The team is also exploring whether the morphing process could be made reversible. “We hope to show that under some conditions we can make these elements responsive — to humidity, for example — when we want to change the shape of an object again,” Sharon says.
The researchers acknowledge funding from the Israeli Ministry of Science, Technology and Space.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Tuesday, Aug. 23, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsfall2022briefings.
ACS Fall 2022 will be a vaccination-required and mask-recommended event for all attendees, exhibitors, vendors and ACS staff who plan to participate in-person in Chicago. For detailed information about the requirement and all ACS safety measures, please visit the ACS website.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Wood warping by 3D printing
Abstract
3D objects composed of 100% wood components were 3D printed using an extrusion-based technique. By predesigning the fiber layout in the printed wood we enable the control of shrinkage distortion beyond natural wood. Thus, resulting in objects that through time dry into programmed warped geometry. In nature, this deformation occurs when changes in moisture content cause unevenly volumetric change due to fiber orientation, in what is known as the wood warping phenomenon. Similar to nature, water evaporation causes volume decrease of the printed object, but in contrast, the printing pathway pattern and flow rate dictate the direction of the alignment and its intensity all of which can be predesigned and affect the resulting structure after drying. It was found that printing parameters such as flow rate and printing pathway, affect the micro and macro morphology of the fully dried objects, and therefore it is possible to design the printing of wet objects that will form different final 3D structures.
Media Contacts
ACS Newsroom
American Chemical Society
newsroom@acs.org
Katie Cottingham
American Chemical Society
k_cottingham@acs.org
Office: 301-775-8455
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















