Unlocking the potential of bacterial gene clusters to discover new antibiotics
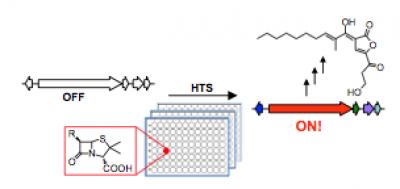
A new method developed at Princeton could lead to the discovery of new antibiotic compounds. Mohammad Seyedsayamdost, an assistant professor of chemistry at Princeton University, has devised a high-throughput screening strategy to activate silent biosynthetic gene clusters, which are not expressed under normal circumstances. The strategy will help researchers explore the products made by these gene clusters and the signals that lead to their activation. Credit: Image courtesy of Mohammad Seyedsayamdost.
Resistance to antibiotics has been steadily rising, posing a threat to public health. Now, a method from Mohammad Seyedsayamdost, an assistant professor of chemistry at Princeton University, may open the door to the discovery of a host of potential drug candidates.
The vast majority of anti-infectives on the market today are bacterial natural products, made by biosynthetic gene clusters. Genome sequencing of bacteria has revealed that these active gene clusters are outnumbered approximately ten times by so-called silent gene clusters.
“Turning these clusters on would really expand our available chemical space to search for new antibiotic or otherwise therapeutically useful molecules,” Seyedsayamdost said.
In an article published last week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Seyedsayamdost reported a strategy to quickly screen whole libraries of compounds to find elicitors, small molecules that can turn on a specific gene cluster. He used a genetic reporter that fluoresces or generates a color when the gene cluster is activated to easily identify positive hits. Using this method, two silent gene clusters were successfully activated and a new metabolite was discovered.
Application of this work promises to uncover new bacterial natural products and provide insights into the regulatory networks that control silent gene clusters.
Seyedsayamdost, M. R. “High-throughput platform for the discovery of elicitors of silent bacterial gene clusters.” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, Early edition doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400019111
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















