New technique unveils 'matrix' inside tissues and tumors
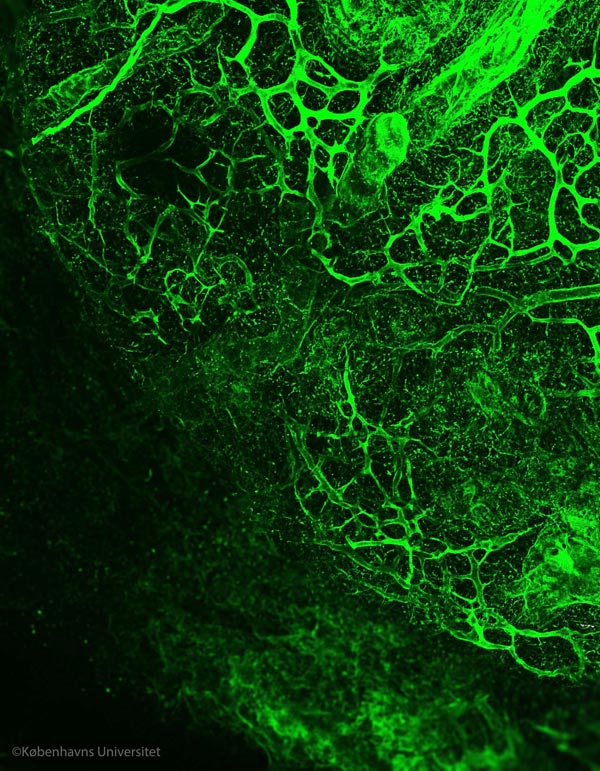
The extracellular matrix structure revealed. The structure of a de-cellularized lymphatic metastasis from a breast cancer. Image by Alejandro Mayorca-Guiliani
“We have developed a technique to obtain intact organ scaffolds and to image them using microscopes. We are the first to image the structures of primary and metastatic tumours as well as healthy organs in this way”, says Prof Erler.
A world of details revealed?Cells which are organised together to form tissues rely on the extracellular matrix as a foundation for attachment, to arrange themselves properly and to sense how to behave when their environment changes. Sometimes this organisation goes wrong and cells grow into tumours. To destroy a tumour, it is essential to know both its structure and the foundation upon which it is built.
This new method was pioneered by postdoctoral fellow Dr Alejandro Mayorca-Guiliani, in Prof Erler's team, who says, “We have isolated the structure that keeps tissues in place and organises the cells inside them. We did this by using existing blood vessels to deliver cell-removing compounds directly to a specific tissue to remove all cells within an organ, while leaving behind an intact scaffold that we could analyse biochemically and microscopically, providing us with the first view of the structure of tumours.”
Imaging expert and co-author Chris Madsen (now at Lund University, Sweden) says “When you remove the cells, the clarity of what you can see through the microscope is much better – you can see the fibres of the matrix more clearly and you can look much deeper into the tissue.”
Matrix biology expert and co-author Thomas Cox (now based at the Garvan Institute, Sydney) says “Because we're removing the cells completely, we can use mass spectrometry to identify and study the components of the matrix – in normal tissue and in tumours – in great detail”.
Understanding cancer progression
This research is an advance in the fields of both cancer research and bioengineering: by using the decellularised organs we can learn much more about how tumours and normal organs are built, and what their differences are. This new technique might even have an impact on organ regeneration and tissue engineering in the future.
“We are now re-introducing cells into our extracellular matrix scaffolds, bringing them back to life, to study how tumours form and how cancer progresses. This is extremely exciting and offers a unique opportunity to study how cells behave in their native environment,” explains Prof Erler.
###
The research is supported by the Danish Cancer Society, an ERC Consolidator Award, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, a European Research Council Consolidator Award, the Ragnar Söderberg Foundation Sweden, Cancerfonden Sweden, the Innovation Foundation Denmark, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Australia and the Danish Council for Independent Research.
Find the published article here: http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















