New species of microalgae discovered
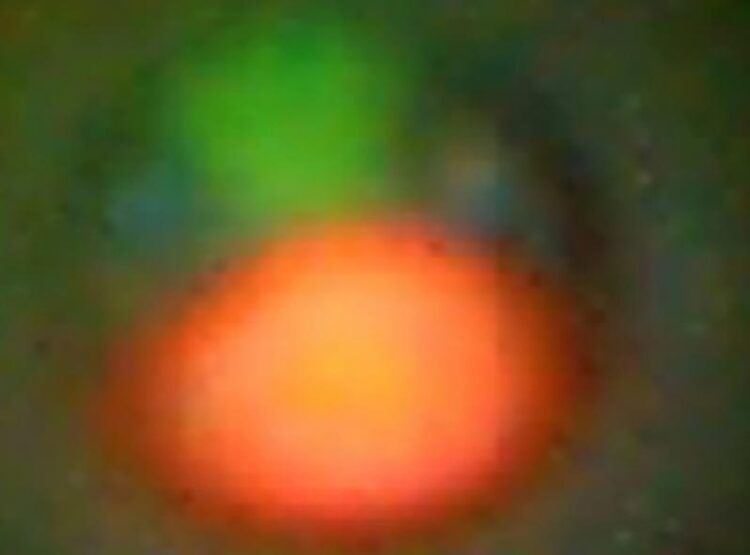

This microscopic fluorescent image of a Medakamo hakoo shows a chloroplast (red), a nucleus (green) and a cytoplasm (blue) in the alga’s cell. The white scale bar indicates 500 nanometers (0.0005 millimeters).
Credit: 2023 Tsuneyoshi Kuroiwa / License: CC BY-NC-ND
Ultrasmall microalgae found in home aquarium could have multiple useful applications.
A new species of microalgae was found in water from a home aquarium. While analyzing DNA samples taken from the algae, researchers from the University of Tokyo discovered Medakamo hakoo, whose DNA sequence didn’t match any on record. This new species is the smallest known freshwater green algae, with inherent qualities which enable it to be cultured stably at high density, meaning it could be effectively used to produce useful products for food and industry.

Credit: 2023 Sachihiro Matsunaga / License: CC BY-NC-ND
If you’ve picked up seaweed on the beach, waded through fronds in a stream or cleaned out a grimy, green fish tank, then you’ll know what algae is. These diverse aquatic organisms thrive on water, light and nutrients and come in all sorts of shapes, colors and sizes. Microalgae are an ultrasmall type of algae which are invisible to the human eye, but a vital part of the Earth’s ecosystem, forming the basis for all aquatic food chains. They have attracted particular attention from researchers and businesses for their ability to capture carbon dioxide, their use as a biofuel, as an alternative source of protein, and more. There are tens of thousands of types of microalgae, which continue to thrive in unexpected places.
“We were very surprised to discover a new species of microalgae in just a regular home aquarium,” said Professor Sachihiro Matsunaga from the Graduate School of Frontier Sciences. “Alga were taken from the water and cultured one by one. The DNA of the alga was fluorescently stained and microscopically observed to find the one with the least amount of DNA per cell. We then sequenced the DNA of that alga and compared it to the DNA of other algae. The results did not match the DNA of any previously reported algae, indicating that it was a new species, and we named it Medakamo hakoo (M. hakoo).”
Microalgae are made up of relatively few genes, and this uncomplicated form makes them useful for researchers trying to identify what roles different genes play and how they could be used. Of the tens of thousands of known microalgae, many remain uncharacterized. Thanks to this latest study, we now know that not only is this a new species, but it also has the smallest known genome of any freshwater algae, as well as other useful qualities.
“M. hakoo contains only one mitochondrion (for producing energy) and one chloroplast (which contains chlorophyll and creates food through photosynthesis), whereas normal plant cells contain multiple mitochondria and chloroplasts. This indicates that it is a green alga with an extremely simple cell structure,” explained Matsunaga. “From our research, we have also speculated that it has an unprecedented DNA structure and a new gene regulatory system. Its cell cycle is also strongly synchronized with the day and night cycle, which is key to effective, stable bioproduction. Due to these inherent qualities and extremely small size, M. hakoo can be effectively cultured at high cell density, making it possible to mass produce substances such as highly functional foods, cosmetics and bio-fuel at a low cost.”
The researchers plan to continue to explore the potential applications for M. hakoo, both in the lab and the wider world. “Aquatic green algae are the originating organisms of today’s land plants. Thanks to this research, we can better understand the minimum number of genes required for an organism to evolve and thrive in diverse environments, which we will continue to study,” said Matsunaga. “In the future, I would like to find ways to collaborate and create useful substances from the mass cultivation of M. hakoo.”
Paper Title:
Shoichi Kato, Osami Misumi, Shinchiro Maruyama, Hisayoshi Nozaki, Yayoi Tsujimoto-Inui, Mari Takasugawa, Shigekatsu Suzuki, Keiko Kuwata, Saki Noda, Nanami Ito, Yoji Okabe, Takuya Sakamoto, Fumi Yagisawa, Tomoko M. Matsunaga, Yoshikatsu Matsubayashi, Haruyo Yamagushi, Masanobu Kawachi, Haruko Kuroiwa, Tsuneyoshi Kuroiwa, Sachihiro Matsunaga “Genomic analysis of an ultrasmall freshwater green alga, Medakamo hakoo”. Communications Biology 6, Article number: 89 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04367-9
Funding:
This work was supported by MXT/JSPS KAKENHI funding, JST-CREST and JST-OPERA grants.
Useful Links:
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences: https://www.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Matsunaga Laboratory: http://park.itc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/matsunaga_lab/english/index.html
Research contacts:
Professor Sachihiro Matsunaga
Department of Integrated Biosciences,
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
The University of Tokyo
5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa City, Chiba 277-8561, Japan
Email: sachi@edu.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mrs. Nicola Burghall
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
Journal: Communications Biology
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-04367-9
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Cells
Article Title: Genomic analysis of an ultrasmall freshwater green alga, Medakamo hakoo
Article Publication Date: 23-Jan-2023
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Simplified diagnosis of rare eye diseases
Uveitis experts provide an overview of an underestimated imaging technique. Uveitis is a rare inflammatory eye disease. Posterior and panuveitis in particular are associated with a poor prognosis and a…

Targeted use of enfortumab vedotin for the treatment of advanced urothelial carcinoma
New study identifies NECTIN4 amplification as a promising biomarker – Under the leadership of PD Dr. Niklas Klümper, Assistant Physician at the Department of Urology at the University Hospital Bonn…
A novel universal light-based technique
…to control valley polarization in bulk materials. An international team of researchers reports in Nature a new method that achieves valley polarization in centrosymmetric bulk materials in a non-material-specific way…





















