How plant cell compartments "chat" with each other
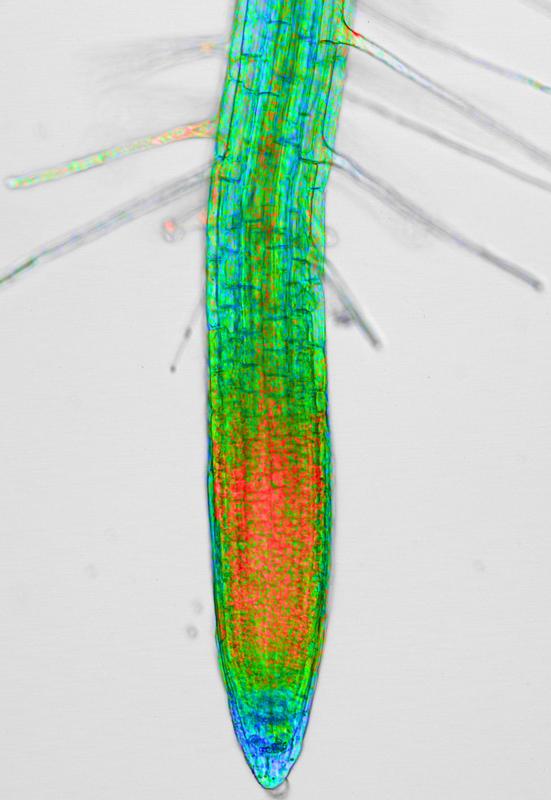
The fluorescent sensor protein provides information on the calcium ion concentration in mitochondria in real time. Blue indicates low, green, medium and red, high concentrations. © Photo: Dr. Stephan Wagner
Plants react to stimuli from their environment by specific responses: If available water becomes limiting, they curb evaporation from their leaves. If a pathogen attacks, they arm themselves with chemical weapons. If a soil fungus wishes to collaborate with a plant root for mutual benefit, both partners discuss their duties.
“All of these fine adjustments require a great deal of communication between the individual compartments of the plant cell,” says Dr. Markus Schwarzlaender, principle investigator of an Emmy Noether group at the Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation at the University of Bonn.
When the various components of plant cells communicate with another, they do not use words but calcium ions, i.e. positively charged calcium atoms, instead.
“The information is encoded in the fluctuations of the calcium concentration of the various cell compartments,” explains Dr. Schwarzlaender. How can a single ion contain and transduce so much information? This is the question scientists have been asking themselves since it became known how various cell compartments “chat” with each other.
The “MICU” protein is a central relay station
The team of Dr. Schwarzlaender, together with scientists from Italy, France, England, Australia and the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research in Cologne and the University of Muenster, have now shed light on this question.
Investigating the cellular power stations (mitochondria) of thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), the scientists discovered that the “MICU” protein fulfills a central role in the control of the calcium ion concentration in the mitochondria.
“In mammals, there is a very similar protein which also regulates the concentration of calcium ions,” says Dr. Stephan Wagner from the team working with Dr. Schwarzlaender. Like a turbocharger, it prompts the mitochondria of mammals to provide more energy.
The scientists speculated that this could be an interesting candidate, but they were taken by surprise when they found the closely related plant-based “MICU” to be a central relay station in the communication system of Arabidopsis. “The two, similar proteins in animals and plants have evidently arisen from a common ancestor but over the course of millennia, they have developed distinct characteristics,” says Dr. Schwarzlaender.
Fluorescing cellular power stations provide information
By destroying the gene with the MICU blueprint in the Arabidopsis genome, the researchers were able to experimentally explore what influence the protein has on the calcium communication of the plant cells. They equipped the mitochondria with a fluorescing sensor protein.
Using the variable fluorescence intensities of the sensor, it was possible to visualize changes in the calcium concentrations of the cellular power stations in the living plants. “We were able to identify a clear influence on the communication of the mitochondria,” reports Dr. Wagner. Knockout of the MICU gene resulted, among other consequences, in modified properties of cell respiration.
“With our findings, we have established a basis for influencing the calcium signals in specific parts of the plant cell,” Dr. Schwarzlaender summarizes. Since Arabidopsis is considered to be an experimental model for plants in general, the findings may be usable in the future for optimizing crops.
Looking ahead the researchers note that if, for example, specific plants could be taught to ally themselves with nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria via modified calcium signals, a large amount of fertilizer used in agriculture may be saved.
Publication: The EF-Hand Ca2+ Binding Protein MICU Choreographs Mitochondrial Ca2+ Dynamics in Arabidopsis, journal “The Plant Cell“, DOI: 10.1105/tpc.15.00509
Contact information:
Dr. Markus Schwarzlaender
Plant Energy Biology Lab
Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation
University of Bonn
Tel. ++49-228-7354266
E-Mail: markus.schwarzlander@uni-bonn.de
http://www.plantcell.org/content/early/2015/11/03/tpc.15.00509.abstract Publication
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bonn.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















