How Fish Can Regenerate Eye Injuries at the Cellular Level
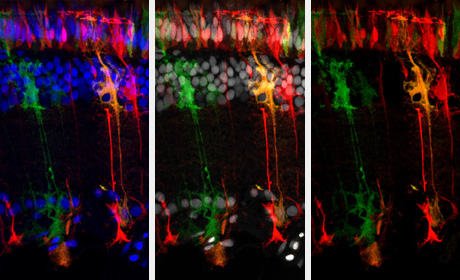
Confocal microscopy image of a section through the medaka fish retina. Single Müller glia and photoreceptor cells are labelled in different colours by a genetic system (red, green, yellow). Atoh7 expression in Müller glia cells leads a regeneration response in the absence of injury, including expansion of the cell soma and neurogenic cluster formation. Image credit: Katharina Lust und Joachim Wittbrodt
Unlike what is possible with the human eye, fish are able to regenerate injuries to the retina at the cellular level. Scientists at Heidelberg University's Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) have now decoded how this regeneration starts, using studies of the model organism of the Medaka fish.
Surprisingly, a single genetic factor triggers two central steps in the process of regeneration – cell division and the differentiation of progenitors into the different retinal cell types. These research results are of great biomedical relevance, according to Prof. Dr Joachim Wittbrodt. They were published in the journal “Development”.
Stem cells in the body can be stimulated in such a way that they start to correct faults autonomously – so far this has merely been science fiction. And yet scientists hope that it will one day be possible to target and replace lost cells in the body.
They focus on the retina of fish, since – unlike humans – fish are able to completely regenerate all retinal nerve cells upon injury. Special glia cells take on the function of stem cells. Why do fish have this ability but not humans, although the human eye also contains these retinal glia cells, also known as Müller cells?
Can the potential of these cells be activated and what factors ultimately stimulate this regenerative reaction? These questions are explored by Prof. Wittbrodt and his team at COS. The Heidelberg scientists have come up with a surprising reply.
Apparently the short pulse of a single genetic factor suffices to stimulate regeneration. The significant factor for cell differentiation is the Atoh7 gene. “We did not think that this key function could be triggered by a single factor,” says Lázaro Centanin, who carried out the study with Prof. Wittbrodt.
Lázaro Centanin explains that the complete regeneration response in the fish eye comprises several steps. First the Müller cells near the injury start to proliferate. The resultant neuronal clusters contain the progenitor cells for the cell types of the retina. In the last step, these progenitors differentiate and turn into the neuronal retinal cells to be restored.
Prof. Wittbrodt adds: “We used the potential of the Müller cells in the Medaka fish in order to test for factors that can evoke exactly this regenerative reaction without any kind of injury.” The different genetic factors employed are relevant either for the increase and growth of cells or play a part in cell differentiation. Joachim Wittbrodt’s research group has established a biological test system enabling the testing of the activity of arbitrary genes specifically in the Müller cells with respect to their regenerative potential.
“We were completely surprised that, with the Atoh7 gene, a single cell differentiation factor fulfils two functions and triggers not only proliferation but also differentiation into different retinal cell types,” says Katharina Lust, the first author of the study that has just been published. To underline the biomedical significance of these research findings, Prof. Wittbrodt points to degenerative retinal diseases that accompany the loss of neuronal cells and lead to blindness in humans.
The factor Atoh7 could either be used to generate retinal progenitor cells for transplantation to the degenerating eye, or also to stimulate the Müller cells directly endogenously. “We still have a long way to go before we can regenerate the human retina by endogenous stimulation of Müller cells. But it is a goal to work towards – and is not mere science fiction,” says the Heidelberg scientist.
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Joachim Wittbrodt
Centre for Organismal Studies
Phone +49 6221 54-6499
jochen.wittbrodt@cos.uni-heidelberg.de
Communications and Marketing
Press Office
Phone +49 6221 54-2311
presse@rektorat.uni-heidelberg.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-heidelberg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Simplified diagnosis of rare eye diseases
Uveitis experts provide an overview of an underestimated imaging technique. Uveitis is a rare inflammatory eye disease. Posterior and panuveitis in particular are associated with a poor prognosis and a…

Targeted use of enfortumab vedotin for the treatment of advanced urothelial carcinoma
New study identifies NECTIN4 amplification as a promising biomarker – Under the leadership of PD Dr. Niklas Klümper, Assistant Physician at the Department of Urology at the University Hospital Bonn…
A novel universal light-based technique
…to control valley polarization in bulk materials. An international team of researchers reports in Nature a new method that achieves valley polarization in centrosymmetric bulk materials in a non-material-specific way…





















