Genetic evidence for single bacteria cause of sepsis identified for the first time
Rather than from a mixture of cooperating bacteria, sepsis seems to originate from a single bacterial cell. Credit: Image credit: Marco R. Oggioni
An international team of academics, including Professor Marco Oggioni from the University of Leicester's Department of Genetics, has studied how localised infections can turn into the dangerous systematic disease sepsis – and has identified for the first time through genetic evidence that a single bacteria could be the cause.
The study, which has been published in the academic journal PLOS Pathogens, examined the events that lead to sepsis by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), a major human pathogen, in mice. They found that in most cases the bacteria causing sepsis was started by a single pneumococcal cell.
The study was an interdisciplinary collaboration between the Departments of Genetics, Infection Immunity and Inflammation and Mathematics at the University of Leicester, Professor Richard Moxon at the University of Oxford and scientists from overseas including the University of Siena.
Professor Oggioni said: “Our data in experimental infection models indicate that we do not need only strategies which target many bacteria when it is too late, but that early intervention schemes which prevent the one-single cell that starts the disease process might provide substantial benefit to the patient.
“In this work we have for the first time provided genetic evidence for a single cell origin of bacterial invasive infection. The scenario was hypothesised over 50 years ago, but so far only phenotypic and statistical evidence could be obtained for this event.”
Under normal circumstances, when different bacteria are used in models of experimental infection of hosts who have not previously encountered the same pathogen, the vast majority is destroyed rapidly by the host's innate immune system.
In the researcher's model, a dose of one million bacteria is needed to induce systemic disease in about half of the hosts in the study.
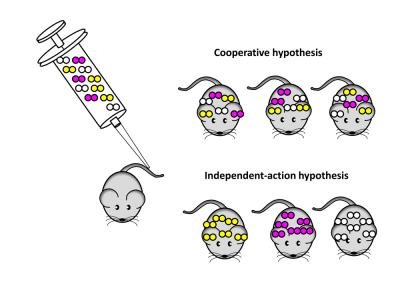
This is in stark contrast to a much lower number of bacteria thought to make up the starting “seed” that leads to the development of systemic infection – and the assumption is that there must be one or more “bottlenecks” in the development of the disease.
To investigate these bottlenecks, the researchers injected mice with a mix of three different variants of S. pneumoniae. About half of the mice developed sepsis and in almost all cases the bacteria causing sepsis were derived from only one of the three variants used in the initial challenge.
Using statistical analysis as well as direct DNA sequencing, the researchers could show that in most cases the bacterial population causing sepsis was started by a single pneumococcal cell.
When the researchers looked closer at how the immune system resists most injected bacteria, they found that macrophages, a type of immune cell that can gobble up bacteria, and specifically macrophages in the spleen, are the main contributors to an efficient immune response to this pathogen.
Their findings suggest that if bacteria survive this initial counter-attack, a single 'founder' bacterium multiplies and re-enters the bloodstream, where its descendants come under strong selective pressure that dynamically shapes the subsequent bacterial population – resulting in the sepsis.
The data also suggests that the single bacterium leading to sepsis has no obvious characteristics that give it an advantage over the 999,999 others, but that random events determine which of the injected bacteria survives and multiplies to cause disease.
It is believed that the findings, suggesting that the development of sepsis starting from a single founding cell which survives the immune system's initial counter-attack in mice, could also potentially apply to human systemic infections.
This information could prove vital to understanding sepsis, as the causes of the disease are still largely unknown to the scientific community.
Dr Oggioni added: “Knowing that there is a moment when a single bacterial cell escapes “normal” immune surveillance at the beginning of each invasive infection is an important paradigm and essential information which, in our opinion, should lead to changes in therapeutic protocols in order to maximise success of treatment outcome.”
The study, 'The Role of Host and Microbial Factors in the Pathogenesis of Pneumococcal Bacteraemia Arising from a Single Bacterial Cell Bottleneck', has been published in the academic journal PLOS Pathogens on Thursday 20 March.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















