Flavins keep a handy helper in their pocket
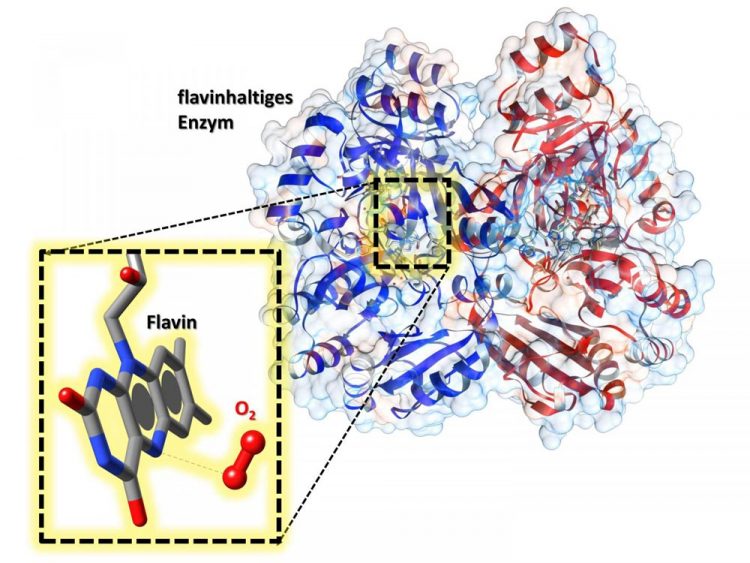
In the active center of the enzyme is a flavin cofactor. In the enlargement we can see that near it, oxygen (O2) is bound -- enabling the flavin to be activated. Source: Robin Teufel, Raspudin Saleem-Batcha
A team headed by Dr. Robin Teufel and Dr. Raspudin Saleem-Batcha of the University of Freiburg at the Center for Biological Systems Analysis has now shown in detail how oxygen interacts with the flavin in an enzyme – revealing for the first time precisely how it works.
The researchers have published their results in the latest Proceedings of the National Academy USA (PNAS).
Flavins play a key role in metabolic processes, in the immune system and in neural development in humans – and are equally important to bacteria, fungi and plants.
Flavoenzymes often require oxygen to function. But until now many of the details of their interaction were not known.
The researchers used x-ray diffraction analysis to show for the first time that oxygen is bound to a special pocket inside the enzyme.
The nature of this compound makes it possible to activate the cofactor – making it essential for the enzyme to work. This knowledge may help, for example, to rationally modify flavoenzymes in the future – in basic research or for biotechnological applications.
###
Original publication:
Raspudin Saleem-Batcha, Frederick Stull, Jacob N. Sanders, Bradley S. Moore, Bruce A. Palfey, K. N. Houk, Robin Teufel: Enzymatic control of dioxygen binding and functionalization of the Flavin cofactor. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. DOI: 10.1073
http://www.
Contact:
Center for Biological Systems Analysis
University of Freiburg
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















