By popular demand
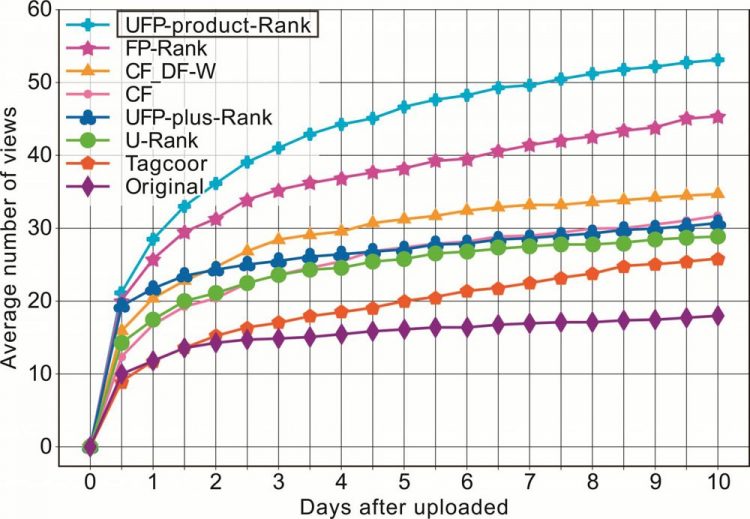
This is a chart to show popularity of posts that use tags recommended by the algorithm. Credit: © 2019 Wang et al.
Computer scientists created a new algorithm to recommend tags for social media posts which should boost the popularity of the post in question. This algorithm takes into account more kinds of information than previous algorithms with a similar goal. The result is a measurably improved view count for posts which use the tags recommended by this new algorithm. Such research could be useful commercially and for other researchers who study online behavior.
Xueting Wang is a postdoctoral researcher at the Yamasaki Laboratory. As a keen user of social media sites, she was puzzled by how different posts by different people achieve notoriety or fade into obscurity. Driven by this curiosity Wang, her colleague Yiwei Zhang and their supervisor, Associate Professor Toshihiko Yamasaki, investigated the relationship between social media content, the tags attached to content and the people who post it.
“It is well-known in our field that tags for social media posts are important,” explained Wang. “It's also known that the nature of these tags, and the relative popularity of the user in question, can impact the popularity of a post — for example the number of views. What I wanted to do was come up with a system to recommend suitable tags for your posts that would demonstrably improve their popularity.”
This is far easier said than done. Computers are exceptional at precisely defined mathematical tasks; however, some of the social concepts explored by the researchers, such as a user's popularity, are too vague for a computer to process directly. Wang and team had to carefully define every aspect of the problem in mathematical terms for an algorithm to be possible.
“We had 60,000 publicly available images with tags, number of views and associated user data from photography website Flickr to experiment with,” continued Wang. “That gave us enough source data to make a system to score different user and image details, and assign numerical values to things. This meant we could perform different functions on the data.”
Wang and team used this data to rank the effective success of a specific tag in contributing to the images view count. Essentially, successful tags were recommended by this process that resulted in a 20-percent boost to the popularity of a post. But what sets their approach apart from others is that it takes into account who created the post. The system cleverly imitates the tagging behavior of people with high social popularity scores to recommend effective tags.
“The algorithm is called the 'user-aware folk popularity rank' and it is the first of its kind to be, as the name suggests, aware of the user in how it recommends tags,” said Wang. “We see from our results that carefully selected tags which express emotional impressions rather than just literal representations of the image content will be more effective. But all the tags the system produces are from an existing pool and it would be good to grow our system so it can generate new ideas.”
There are clear commercial applications for the user-aware folk popularity rank and the team already has some commercial partners taking on its recommendations to help promote their outputs. However, a good scientist's work is never done and Wang intends to improve the effectiveness of the system as well as implement greater autonomy so it can generate tags of its own. She also hopes social media researchers could use these ideas to explore things like what makes someone popular online to begin with.
###
Conference proceedings article
Xueting Wang, Yiwei Zhang and Toshihiko Yamasaki. User-Aware Folk Popularity Rank: User-Popularity-Based Tag Recommendation That Can Enhance Social Popularity. Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia
https:/
DOI: 10.1145/3343031.3350920
This work was partially financially supported by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research Numbers JP19K20289, JP19J22939 and JP18H03339 from JSPS, and by CREST JPMJCR1686.
Related Links
Aizawa-Yamasaki laboratory
https:/
Department of Information and Communication Engineering
https:/
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology
https:/
Research Contact
Project Researcher Xueting Wang
Department of Information and Communication Engineering, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-6761
Email: xt_wang@hal.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press Contact
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-0876
Email: press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at https:/
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















