One in, two out: Simulating more efficient solar cells
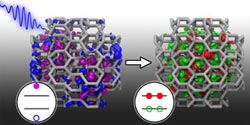
Computer simulations show that when a light particle (blue wave on left) hits a crystal of a high-pressure form of silicon, it releases two electron-hole pairs (red circles/green rings), which generate electric current. (Stefan Wippermann/UC Davis photo) <br>
Solar cells are based on the photoelectric effect: a photon, or particle of light, hits a silicon crystal and generates a negatively charged electron and a positively charged hole. Collecting those electron-hole pairs generates electric current.
Conventional solar cells generate one electron-hole pair per incoming photon, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency of 33 percent. One exciting new route to improved efficiency is to generate more than one electron-hole pair per photon, said Giulia Galli, professor of chemistry at UC Davis and co-author of the paper.
“This approach is capable of increasing the maximum efficiency to 42 percent, beyond any solar cell available today, which would be a pretty big deal,” said lead author Stefan Wippermann, a postdoctoral researcher at UC Davis.
“In fact, there is reason to believe that if parabolic mirrors are used to focus the sunlight on such a new-paradigm solar cell, its efficiency could reach as high as 70 percent,” Wippermann said.
Galli said that nanoparticles have a size of nanometers, typically just a few atoms across. Because of their small size, many of their properties are different from bulk materials. In particular, the probability of generating more than one electron-hole pair is much enhanced, driven by an effect called “quantum confinement.” Experiments to explore this paradigm are being pursued by researchers at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Golden, Colo., as well as at UC Davis.
“But with nanoparticles of conventional silicon, the paradigm works only in ultraviolet light,” Wippermann said. “This new approach will become useful only when it is demonstrated to work in visible sunlight.”
The researchers simulated the behavior of a structure of silicon called silicon BC8, which is formed under high pressure but is stable at normal pressures, much as diamond is a form of carbon formed under high pressure but stable at normal pressures.
The computer simulations were run through the National Energy Research Scientific Supercomputing Center at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, which granted the project 10 million hours of supercomputer time.
The simulations demonstrated that nanoparticles of silicon BC8 indeed generate multiple electron-hole pairs per photon even when exposed to visible light.
“This is more than an academic exercise. A Harvard-MIT paper showed that when normal silicon solar cells are irradiated with laser light, the energy the laser emits may create a local pressure high enough to form BC8 nanocrystals. Thus, laser or chemical pressure treatment of existing solar cells may turn them into these higher-efficiency cells,” said co-author Gergely Zimanyi, professor of physics at UC Davis.
Other authors of the paper are Marton Voros and Adam Gali at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary.
The work was funded by a National Science Foundation Solar Collaborative grant awarded to Zimanyi, Galli and colleagues at UC Davis and UC Santa Cruz in 2011. The project brings together experts in material science, chemistry, computer simulations and statistics to develop new approaches to solar power.
About UC Davis
For more than 100 years, UC Davis has engaged in teaching, research and public service that matter to California and transform the world. Located close to the state capital, UC Davis has more than 33,000 students, more than 2,500 faculty and more than 21,000 staff, an annual research budget of nearly $750 million, a comprehensive health system and 13 specialized research centers. The university offers interdisciplinary graduate study and more than 100 undergraduate majors in four colleges — Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Biological Sciences, Engineering, and Letters and Science. It also houses six professional schools — Education, Law, Management, Medicine, Veterinary Medicine and the Betty Irene Moore School of Nursing.
Media contact(s):
Giulia Galli, Chemistry, (530) 754-9554, gagalli@ucdavis.edu
Stefan Wippermann, Chemistry, wippermann@ucdavis.edu
Gergely Zimanyi, Physics, (530) 400-3936, gtzimanyi@ucdavis.edu
Andy Fell, UC Davis News Service, (530) 752-4533, ahfell@ucdavis.edu
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucdavis.eduAll latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















