UCSB physicists demonstrate the quantum von Neumann architecture
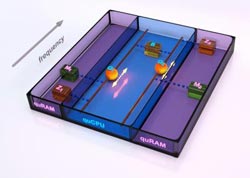
The quantum von Neumann machine: Two qubits are coupled to a quantum bus, realizing a quCPU. Each qubit is accompanied by a quantum memory as well as a zeroing register. The quantum memories together with the zeroing register realize the quRAM. Credit: Peter Allen, UCSB<br>
UCSB physicists have demonstrated a quantum integrated circuit that implements the quantum von Neumann architecture. In this architecture, a long-lived quantum random access memory can be programmed using a quantum central processing unit, all constructed on a single chip, providing the key components for a quantum version of a classical computer.
The UCSB hardware is based on superconducting quantum circuits, and must be cooled to very low temperatures to display quantum behavior. The architecture represents a new paradigm in quantum information processing, and shows that quantum large-scale-integration is within reach.
The quantum integrated circuit includes two quantum bits (qubits), a quantum communication bus, two bits of quantum memory, and a resetting register comprising a simple quantum computer. “Computational steps take a few billionths of a second, comparable to a classical computer, but the great power is that a quantum computer can perform a large number of calculations simultaneously,” said Matteo Mariantoni, postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Physics. “In our new UCSB architecture we have explored the possibility of writing quantum information to memory, while simultaneously performing other quantum calculations.
“On the quantum von Neumann architecture, we were able to run the quantum Fourier transform and a three-qubit Toffoli gate –– key quantum logic circuits for the further development of quantum computing,” said Mariantoni.
The UCSB experiment was pursued primarily by Mariantoni, under the direction of Andrew N. Cleland and John M. Martinis, both professors of physics. Mariantoni was supported in this work by an Elings Prize Fellowship in Experimental Science from UCSB's California NanoSystems Institute.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucsb.eduAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















