Chirality in 'real-time'
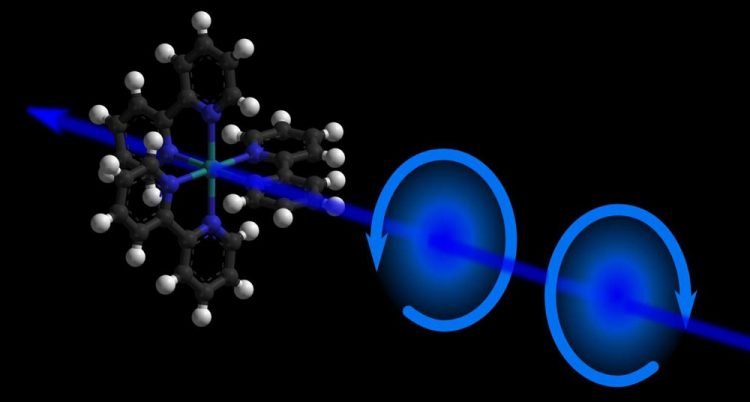
An illustration of chirality in a molecule. Credit: M. Oppermann, EPFL
The method commonly used to detect enantiomers is circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. It exploits the fact that light polarized into a circular wave (like a whirlpool) is absorbed differently by left-handed and right-handed enantiomers. Steady-state CD spectroscopy is a major structural tool in (bio)chemical analysis.
During their function, biomolecules undergo structural changes that affect their chiral properties. Probing these in real-time (i.e. between 1 picosecond and 1 nanosecond) provides a view of their biological function, but this has been challenging in the deep-UV spectrum (wavelengths below 300 nm) where most biologically relevant molecules such as amino acids, DNA and peptide helices absorb light.
The limitations are due to the lack of adequate sources of pulsed light and of sensitive detection schemes. But now, the group of Majed Chergui at the Lausanne Centre for Ultrafast Science (EPFL) has developed a setup that allows the visualization of the chiral response of (bio)molecules by CD spectroscopy with a resolution of 0.5 picoseconds.
The setup uses a photoelastic modulator, which is an optical device that can control the polarization of light. In this system, the modulator permits shot-to-shot polarization switching of a 20 kHz femtosecond pulse train in the deep-UV range (250-370 nm). It is then possible to record changes in the chirality of molecules at variable time-delays after they are excited with a short laser pulse.
“Amino acid residues and DNA bases absorb light below 300 nm,” says Malte Oppermann, the paper's first author. “This set-up is the first to cover this region, and we successfully tested it on a model molecular system. Our next aim is to move on to larger biosystems, like DNA oligomers.”
###
Other contributors
University of Geneva
University of Zurich
Reference
Malte Oppermann, Benjamin Bauer, Thomas Rossi, Francesco Zinna, Jan Helbing, Jérôme Lacour, Majed Chergui. Ultrafast broadband circular dichroism in the deep ultraviolet. Optica 6(1): 56-60, 10 January 2019. DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000056
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















