Astronomers find new evidence for the violent demise of sun-like stars
New York’s Rochester Institute of Technology and University of Rochester to present results
Two astronomers have used NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory to discover a shell of superheated gas around a dying star in the Milky Way galaxy.
Joel Kastner, professor of imaging science at the Rochester Institute of Technology, and Rodolpho Montez, a graduate student in physics and astronomy at the University of Rochester, will present their results today at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Minneapolis. Their discovery shows how material ejected at two million miles per hour during the final, dying stages of sun-like stars can heat previously ejected gas to the point where it will emit X-rays. The study also offers new insight into how long the ejected gas around dying stars can persist in such a superheated state.
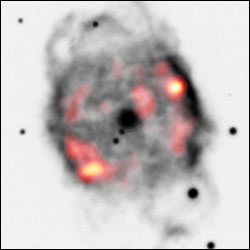
According to Kastner, the hot gas shows up in high-resolution Chandra X-ray images of the planetary nebula NGC 40, which is located about 3,000 light years away from Earth in the direction of the constellation Cepheus. “Planetary nebulae are shells of gas ejected by dying stars,” Kastner explains. “They offer astronomers a ’forecast’ of what could happen to our own sun about five billion years from now–when it finally exhausts the reservoir of hydrogen gas at its core that presently provides its source of nuclear power.”
In his research, Montez discovered the X-ray emitting shell in NGC 40 by generating an image that uses only specific energy-selected X-rays–revealing a ring of superheated gas that lies just within the portions of the nebula that appear in optical and infrared images.
“This hot bubble of gas vividly demonstrates how, as a planetary nebula forms, the gas ejection process of the central, dying star becomes increasingly energetic,” Kastner notes. “Mass ejection during stellar death can result in violent collisions that can heat the ejected gas up to temperatures of more than a million degrees.”
The detection of X-rays from NGC 40 adds to a growing list of such discoveries by Chandra and its European counterpart, the XMM-Newton X-ray satellite observatory. Kastner and Montez (along with collaborators Orsola de Marco, of the American Museum of Natural History in New York, and Noam Soker, of the Technion Institute in Haifa, Israel) have studied these previous X-ray observations of planetary nebulae, and find that the X-ray and infrared output of such objects is closely coupled.
“The connection between X-ray and infrared emission seems to show that the hot bubble phase is restricted to early times in stellar death, when a planetary nebula is quite young and the dust within it is still relatively warm,” says Montez about his observations.
The correspondence indicates that the production of superheated gas is a short-lived phase in the life of a planetary nebula, although Kastner cautions that additional Chandra and XMM-Newton observations are required to test this idea.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.rit.eduAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















