New nanofiber marks important step in next generation battery development
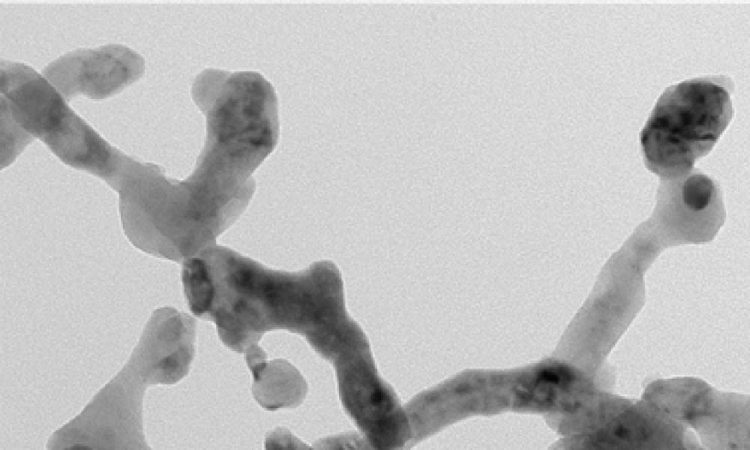
This is a 20 nanometer double perovskite nanofiber that can be used as a highly efficient catalyst in ultrafast oxygen evolution reactions -- one of the underlying electrochemical processes in hydrogen-based energy and the newer metal-air batteries. Credit: Georgia Tech
Materials researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology have created a nanofiber that could help enable the next generation of rechargeable batteries and increase the efficiency of hydrogen production from water electrolysis.
In a study that was published February 27 in Nature Communications and was sponsored by the National Science Foundation, the researchers describe the development of double perovskite nanofiber that can be used as a highly efficient catalyst in ultrafast oxygen evolution reactions – one of the underlying electrochemical processes in hydrogen-based energy and the newer metal-air batteries.
“Metal-air batteries, such as those that could power electric vehicles in the future, are able to store a lot of energy in a much smaller space than current batteries,” said Meilin Liu, a Regents Professor in the Georgia Tech School of Materials Science and Engineering. “The problem is that the batteries lack a cost-efficient catalyst to improve their efficiency. This new catalyst will improve that process.”
Perovskite refers to the crystal structure of the catalyst the researchers used to form the nanofibers.
“This unique crystal structure and the composition are vital to enabling better activity and durability for the application,” Liu said.
During the synthetization process, the researchers used a technique called composition tuning – or “co-doping” – to improve the intrinsic activity of the catalyst by approximately 4.7 times. The perovskite oxide fiber made during the electrospinning process was about 20 nanometers in diameter – which thus far is the thinnest diameter reported for electrospun perovskite oxide nanofibers.
The researchers found that the new substance showed markedly enhanced oxygen evolution reaction capability when compared to existing catalysts. The new nanofiber's mass-normalized catalytic activity improved about 72 times greater than the initial powder catalyst, and 2.5 times greater than iridium oxide, which is considered a state of the art catalyst by current standards.
That increase in catalytic activity comes in part from the larger surface area achieved with nanofibers, the researchers said. Synthesizing the perovskite structure into a nanofiber also boosted its intrinsic activity, which also improved how efficiently it worked as a catalyst for oxygen evolution reactions (OER).
“This work not only represents an advancement in the development of highly efficient and durable electrocatalysts for OER but may also provide insight into the effect of nanostructures on the intrinsic OER activity,” the researchers wrote.
Beyond its applicability in the development of rechargeable metal air batteries, the new catalyst could also represent the next step in creating more efficient fuel cell technologies that could aid in the creation of renewable energy systems.
“Solar, wind, geothermal – those are becoming very inexpensive today. But the trouble is those renewable energies are intermittent in nature,” Liu said. “When there is no wind, you have no power. But what if we could store the energy from the sun or the wind when there's an excess supply. We can use that extra electricity to produce hydrogen and store that energy for use when we need it.”
That's where the new nanofiber catalysts could make a difference, he said.
“To store that energy, batteries are still very expensive,” Liu said. “We need a good catalyst in order for the water electrolysis to be efficient. This catalyst can speed up electrochemical reactions in water splitting or metal air batteries.”
###
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant Nos. DMR-1410320 and TG-DMR140083. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
CITATION: Bote Zhao, Lei Zhang, Dongxing Zhen, Seonyoung Yoo, Yong Ding, Dongchang Chen, Yu Chen, Qiaobao Zhang, Brian Doyle, Xunhui Xiong and Meilin Liu, “A tailored double perovskite nanofiber catalyst enables ultrafast oxygen evolution,” (Nature Communications, 2017). http://dx.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















