With new design, bulk semiconductor proves it can take the heat
While long valued for high-temperature applications, the bulk alloy semiconductor SiGe hasn't lent itself to broader adoption because of its low thermoelectric performance and the high cost of Germanium. A novel nanotechnology design created by researchers from Boston College and MIT has shown a 30 to 40 percent increase in thermoelectric performance and reduced the amount of costly Germanium. Credit: Nano Letters<br>
The intense interest in harvesting energy from heat sources has led to a renewed push to discover materials that can more efficiently convert heat into electricity. Some researchers are finding those gains by re-designing materials scientists have been working with for years.
A team of Boston College and MIT researchers report developing a novel, nanotech design that boosts the thermoelectric performance of a bulk alloy semiconductor by 30 to 40 percent above its previously achieved figure of merit, the measuring stick of conversion efficiency in thermoelectrics.
The alloy in question, Silicon Germanium, has been valued for its performance in high-temperature thermoelectric applications, including its use in radioisotope thermoelectric generators on NASA flight missions. But broader applications have been limited because of its low thermoelectric performance and the high cost of Germanium.
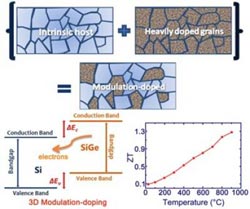
Boston College Professor of Physics Zhifeng Ren and graduate researcher Bo Yu, and MIT Professors Gang Chen and Mildred S. Dresselhause and post-doctoral researcher Mona Zebarjadi, report in the journal Nano Letters that altering the design of bulk SiGe with a process borrowed from the thin-film semiconductor industry helped produce a more than 50 percent increase in electrical conductivity.
The process, known as a 3D modulation-doping strategy, succeeded in creating a solid-state device that achieved a simultaneous reduction in the thermal conductivity, which combined with conductivity gains to provide a high figure of merit value of ~1.3 at 900 °C.
“To improve a material's figure of merit is extremely challenging because all the internal parameters are closely related to each other,” said Yu. “Once you change one factor, the others may most likely change, leading to no net improvement. As a result, a more popular trend in this field of study is to look into new opportunities, or new material systems. Our study proved that opportunities are still there for the existing materials, if one could work smartly enough to find some alternative material designs.”
Ren pointed out that the performance gains the team reported compete with the state-of-the-art n-type SiGe alloy materials, with a crucial difference that the team's design requires the use of 30 percent less Germanium, which poses a challenge to energy research because of its high cost. Lowering costs is crucial to new clean energy technologies, he noted.
“Using 30 percent less Germanium is a significant advantage to cut down the fabrication costs,” said Ren. “We want all the materials we are studying in the group to help remove cost barriers. This is one of our goals for everyday research.”
The collaboration between Ren and MIT's Chen has produced several breakthroughs in thermoelectric science, particularly in controlling phonon transport in bulk thermoelectric composite materials. The team's research is funded by the Solid State Solar Thermal Energy Conversion Center.
The 3STEC Center is part of the U.S. Department of Energy's Energy Frontier Research Center program, which is aimed at advancing fundamental science and developing materials to harness heat from the sun and convert the heat into electricity via solid-state thermoelectric and thermophotovoltaic technologies.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.bc.eduAll latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















