Researchers employ antennas for angstrom displacement sensing
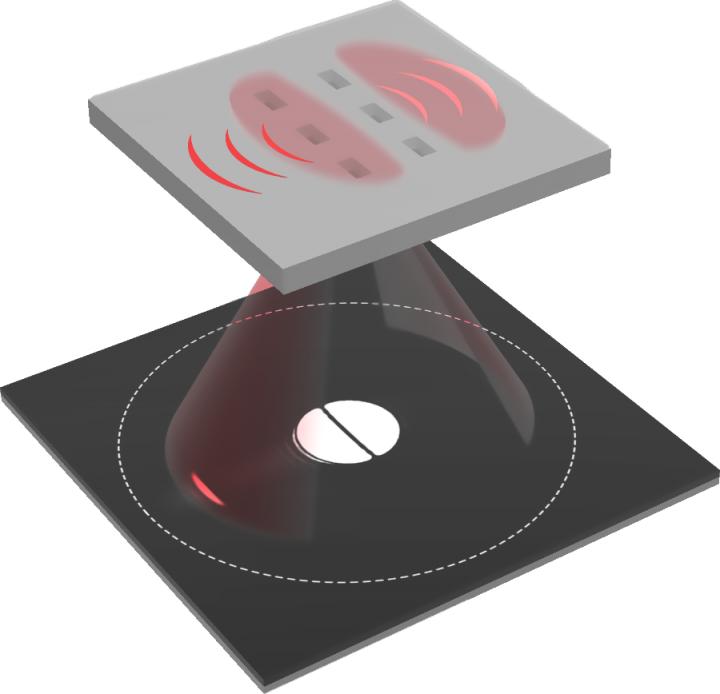
Schema of the near-field interaction between the antennas and incident light field. Credit: ZANG Tianyang et al.
Optical metrology is of particular significance for it allows measurements of distance or displacement in a noncontact high-precision way.
However, despite of the wide application in longitudinal displacement measurement of interferometric method, such as laser radar, laser ranging and small vibration measurement, lateral displacement perpendicular to the direction of the beam is hard to be detected through conventional methods.
The researchers presented a novel technique based on directional excitation of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs).
They first excited asymmetric SPPs with a pair of optical slot antennas under the illumination of the focused Hermite-Gaussion (HG) (1,0) mode light. Then, by detecting the SPPs leakage at the back-focal plane of an oil-immersed objective, they sensitively measured the transverse displacement.
Unlike the previous strategy to retrieve the free scattering signals, which remains challenging even when employing a weak measurement technique, the SPPs leakage pattern is spatially separated from the forward scattering of the slot antennas, and thus could be utilized to monitor displacements in the back-focal plane.
The resolution of their system reaches subwavelength level (~0.3 nm).
However, the extreme resolution could be down to angstrom level. It is potentially applicable in superresolution microscopy, semiconductor lithography, and calibration of nanodevices.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…





















