World’s first UV ’ruler’ sizes up atomic world
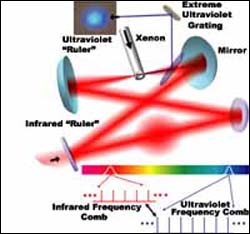
The new JILA ultraviolet "ruler" is made by exposing xenon gas atoms to a special type of infrared laser light called a femtosecond frequency "comb."
The world’s most accurate “ruler” made with extreme ultraviolet light has been built and demonstrated with ultrafast laser pulses by scientists at JILA, a joint institute of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado at Boulder.
The new device, which consistently generates pulses of light lasting just femtoseconds (quadrillionths of a second, or millionths of a billionth of a second) in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum, will be described in the May 20 issue of Physical Review Letters.*
The device is expected to become an important tool for ultraprecise measurements in many fields of science, including chemistry, physics and astronomy. A ruler made with shorter wavelengths of light makes it possible to “see” more precise differences than ever before in the energy levels of light emissions that identify specific atoms, in the timing of chemical reactions, or, if additional applications are developed, in the dimensions of certain nanometer-scale objects. The new device also can be compared to a camera with ultrafast shutter speeds and consistent shot-to-shot frame speed and stability, allowing scientists to take real-time “pictures” of finer structures and dynamics. By combining many such pictures at a high speed, scientists can gain a more detailed understanding of many phenomena.
“This ultraviolet light source has a spectacularly high resolution,” says Jun Ye, a NIST Fellow who leads the JILA research group. “On the technological side, the system we used to produce this light is simple and low cost, without active amplifiers.”
The new laser device generates a “frequency comb,” so-called because the frequency spectrum–a graphical representation of the pattern made by many successive laser pulses building on each other–looks like the evenly spaced teeth of a hair comb. (See graphic.) The new comb is a short-wavelength version of the optical frequency combs that in recent years have enabled demonstrations of optical atomic clocks, which are expected to be as much as 100 times more accurate than today’s microwave-based atomic clocks. A femtosecond comb, because of its high speed (or repetition rate), has the finest teeth of any optical ruler.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nist.govAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















