Ultrafast laser speeds up quest for atomic control
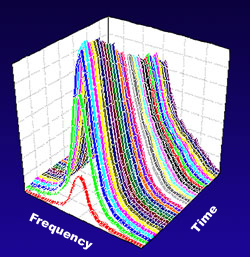
It’s the scientific equivalent of having your cake and eating it too. A team of researchers from JILA, a joint institute of the Commerce Department’s National Institute of Standards and Technology and the University of Colorado at Boulder, has developed an efficient, low-cost way to measure the energy levels of atoms in a gas with extremely high accuracy, and simultaneously detect and control transitions between the levels as fast as they occur. The technique is expected to have practical applications in many fields including astrophysics, quantum computing, chemical analysis, and chemical synthesis.
Described in the Nov. 18 online issue of Science Express,* the method uses ultrafast pulses of laser light like a high speed movie camera to record in real-time the energy required to boost an atom’s outer electrons from one orbital pattern to another. The pulses are so short that scientists can track precisely the fraction of atoms in each energy state and how those populations change with time. Moreover, the atoms respond to subsequent laser pulses cumulatively–the energy adds up over time–which allows fine-tuning to affect specific orbital patterns of interest with a much lower power laser than usual.
All of chemistry depends on the configurations of these outer electrons. The technique promises to make it easier for scientists to systematically understand the radiation “signatures” (or spectra) given off by atoms and molecules as their electrons jump between different energy levels. Ultimately, it should allow improved control of the complex chain of events that combines atoms into desired compounds.
The JILA team is a world leader in applying so-called “frequency combs” to practical science problems. The laser system used in the current work emits a hundred thousand different infrared frequencies at once in individual pulses lasting just femtoseconds (quadrillionths of a second). The JILA researchers used the laser to precisely study the electron energy levels within an ultracold gas of rubidium atoms. The ability to probe atoms with many different laser frequencies simultaneously and to monitor atom responses in real time should allow scientists to study and control systems in a vastly more efficient and precise manner.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nist.govAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















