Alexandrite laser crystals from Europe for space applications
The alexandrite crystals from the GALACTIC project were grown by Optomaterials and coated by Altechna to withstand the harsh conditions in space.
Photo: LZH
Alexandrite laser crystals are well suited for use in earth observation satellites.
They are robust and enable laser systems with a tunable output wavelength. In the European Horizon 2020 project GALACTIC, the partners Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH), Optomaterials S.r.l. (Italy) and Altechna (Lithuania) have now succeeded in establishing a solely European supply chain for alexandrite laser crystals, which can be used for space applications.
The Italian partner Optomaterials produces competitive crystals, which the Lithuanian company Altechna provides with a special coating. To achieve the necessary properties for space-applications, Altechna has developed special coating designs and processes based on ion beam and magnetron sputtering processes.
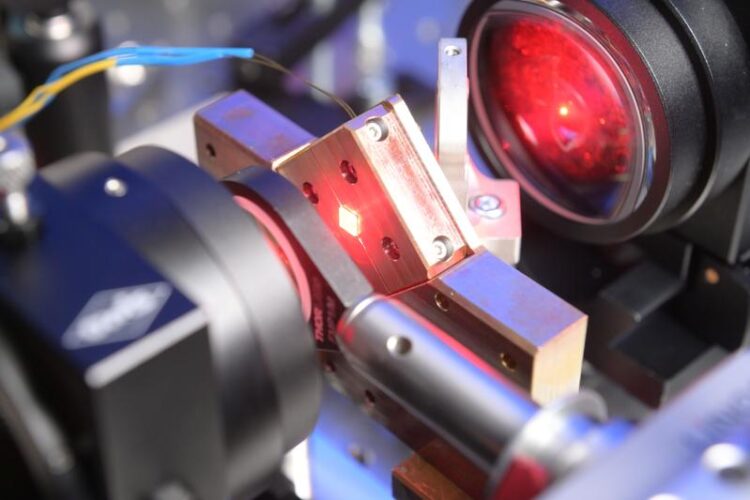
Proven: Space suitability

Photo: LZH
Scientists at the LZH thoroughly tested the crystals in special laser systems. They have designed these systems with future applications in mind. The demonstrators could lay the foundation for new laser-based measuring instruments. The LZH’s scientists exposed the Alexandrite crystals to proton and gamma radiation and ran them through several temperature cycles typical for space applications. Before and after these environmental tests, they have characterized the crystals in terms of their transmission properties and laser performance, among other things. Since the environmental tests did not significantly change the measured parameters, the space suitability could be demonstrated. In addition, the researchers showed that the laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of the crystals is equal to – or even exceeds – top products on the world market.
Crystals now ready for the market: GALACTIC has reached TRL 6
The GALACTIC team has thus successfully raised the Technology Readiness Level (TRL) of space-qualified alexandrite crystals from Europe from 4 to 6 and have made the crystals ready for the market.
Special properties for more precise data
Alexandrite crystals have very good thermal conductivity and fracture strength. Therefore, they are suitable for use in high power laser systems and are robust enough to withstand the harsh conditions in space. Since the crystals can be used to tune the output wavelength of laser systems, they could form the basis of new types of laser-based measuring instruments for Earth observation satellites. Such instruments could be used to collect more precise climate-relevant data on the state of the atmosphere or vegetation.
About GALACTIC
In the project “High Performance Alexandrite Crystals and Coatings for High Power Space Applications” (GALACTIC), the Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. together with Altechna and Optomaterials S.r.l. have established an independent, purely European supply chain for alexandrite laser crystals. GALACTIC was funded by the research and innovation program “Horizon 2020” of the European Union under funding code No. 870427. GALACTIC was coordinated by the LZH.
Originalpublikation:
S. Unland, R. Kalms, P. Wessels, D. Kracht, and J. Neumann, “High-performance cavity-dumped Q-switched Alexandrite laser CW diode-pumped in double-pass configuration,” Opt. Express 31, 1112-1124 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.478628
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















