Latest News
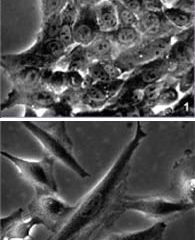
Akt kinase "fuels" migration of tumor cells
Although cells generally tend to “stay at home”, they may sometimes wish to take a look elsewhere, and this wandering has a whole range of consequences. During embryonic development, cells must migrate to give birth to new tissues. This roving spirit is essential to the modeling of the future living organism. In contrast, when tumor cells acquire the capacity to move around and invade other tissues, there is a risk that metastases will develop, thus rendering the treatment of cancer more difficult.

Vehicle poised to advance exploration on Mars
Pioneering research carried out by Kingston University is helping to pave the way for a manned mission to Mars. A project team based at the University’s School of Engineering has developed a robotic micro-rover to travel the Martian surface to find out whether humans could live in the Red Planet’s hostile environment.
Named Endurance, the small self-propelled vehicle will be powered by the sun’s rays and equipped to drill beneath the surface to find out if life exists on Mars in the form of
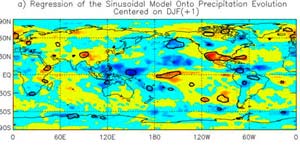
Nasa Discovers aSoggy Secret of El Niño
NASA-funded researchers have discovered El Niño’s soggy secret. When scientists identified rain patterns in the Pacific Ocean, they discovered the secret of how El Niño moves rainfall around the globe during the life of these periodic climate events when waters warm in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
The results may help scientists improve rainfall forecasts around the globe during the life of an El Niño, and may also offer new insights into how an El Niño develops.
The findings were hi

Growing world urban populations threatened by massive earthquakes
A new study by a University of Colorado at Boulder geological sciences professor suggests one earthquake causing up to 1 million fatalities on Earth each century could occur unless more earthquake-resistant construction materials are implemented.
Professor Roger Bilham’s conclusions are based on a study of the world’s urban population growth in the 21st century, including the number of rapidly expanding “supercities” and their locations close to major fault lines that have caused past tembl

Ears can’t hear when special sensory cells don’t stay ’quiet’
The death of sensory hair cells when they try to multiply suggests need for caution in attempts to restore many kinds of lost cells through gene therapy
Researchers may have found a link between progressive hearing loss and a gene called p19Ink4d (Ink4d), according to results of a study that measured loss of hearing in mice lacking that gene. Normally, the Ink4d gene keeps healthy cells “quiet” – from inappropriately dividing.
Mice lacking the Ink4d gene become progressively

Livermore researchers discover uncertainties in satellite data hamper detection of global warming
Using a new analysis of satellite temperature measurements, scientists from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have determined that uncertainties in satellite data are a significant factor in studies attempting to detect human effects on climate.
Since 1979, Microwave Sounding Units (MSUs) have been flown on 12 different polar-orbiting weather satellites operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. MSU instruments measure the microwave emissions of oxygen mo











