Latest News

Electron nanodiffraction technique offers atomic resolution imaging
A new imaging technique that uses electron diffraction waves to improve both image resolution and sensitivity to small structures has been developed by scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The technique works on the same principle as X-ray diffraction, but can record structure from a single nanostructure or macromolecule.
Determining the structure of materials — such as protein crystals — is currently performed using X-ray diffraction. However, many small structur
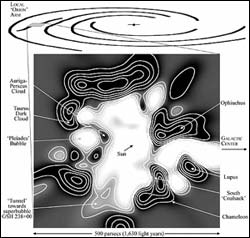
3-D map of local interstellar space shows sun lies in middle of hole piercing galactic plane
The first detailed map of space within about 1,000 light years of Earth places the solar system in the middle of a large hole that pierces the plane of the galaxy, perhaps left by an exploding star one or two million years ago.
The new map, produced by University of California, Berkeley, and French astronomers, alters the reigning view of the solar neighborhood. In that picture, the sun lies in the middle of a hot bubble – a region of million-degree hydrogen gas with 100-1,000 times fewer

RHESSI uncovers secret to cataclysmic explosions known as gamma-ray bursts
University of California, Berkeley’s RHESSI satellite, launched last year by NASA, was snapping X-ray pictures of solar flares in December when it caught an extremely bright background gamma-ray burst, revealing a novel physical feature of these gamma rays – their polarization.
The result sheds new light on the driving force behind these mysterious explosions.
Gamma-ray bursts are mysterious flashes of gamma-ray photons that pop off about once a day randomly in the sky, briefl

Seaweed uses chemical warfare to fight microbes
Scientists have discovered that seaweeds defend themselves from specific pathogens with naturally occurring antibiotics. The finding helps explain why some seaweeds, sponges and corals appear to avoid most infections by fungi and bacteria, according to a study published May 19 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Seaweeds live in constant contact with potentially dangerous microbes, and they have apparently evolved a chemical defense to help resist disease,” said lead author

Project pairs coal with fuel cells to create cleaner, more efficient power
Ohio University engineers are leading one of the first comprehensive efforts to examine how fuel cell technology could pave the way for cleaner coal-fired power plants. Supported by a $4 million U.S. Department of Energy grant secured by the Ohio Congressional delegation, the project aims to find ways to use coal – the environmentally dirtiest but most abundant fossil fuel in the world — to harness high-efficiency fuel cells.
Most government-sponsored energy research is focused on using nat

New results force scientists to rethink single-molecule wires
Single-molecule switches have the potential to shrink computing circuits dramatically, but new results from the Arizona State University lab that first described how to wire a single molecule between gold contacts now show that laboratory-standard wired molecules have an unavoidable tendency to “blink” randomly.
In the May 30, 2003, Science, Stuart Lindsay and colleagues identify the cause of this blinking behavior as random, temporary breaks in the chemical bond between the wired molecule