Nanotube ’Peapods’ Exhibit Surprising Electronic Properties
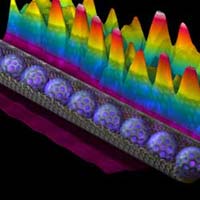
Image: D. Hornbaker and A. Yazdani
In yet another small step toward building nanoscale devices, scientists have determined that nanotube peapods — minute straws of carbon filled with spherical carbon molecules known as buckyballs — have tunable electronic properties. Published online by the journal Science,the findings suggest that stuffing the straws provides greater control over the electronic states of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT).
Using a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope, Ali Yazdani of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and colleagues imaged the physical structure of individual peapods (right). They mapped the motion of electrons within the pipes and, as Yazdani explains, showed “that an ordered array of encapsulated molecules can be used to engineer electron motion inside nanotubes in a predictable way.” Though the harbored buckyballs modify the electronic properties of the nanotube, the atomic structure of the straw remains unchanged.
The researchers also utilized the microscope to move the buckyballs, which allowed them to compare the same section of a SWNT when it was filled and unfilled. “The encapsulated balls have a much stronger effect on the electronic structure of the tube than we had expected,” says study co-author Eugene Mele of the University of Pennsylvania. Indeed, the authors conclude that their calculation not only shows how a peapod’s electronic properties differ from those of its constituent parts, “it also provides possible design rules for proposing hybrid structures having a specific type of electronic functionality.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.sciam.com/news/010402/1.htmlAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…





















