Uranium-immobilizing bacteria in clay rock
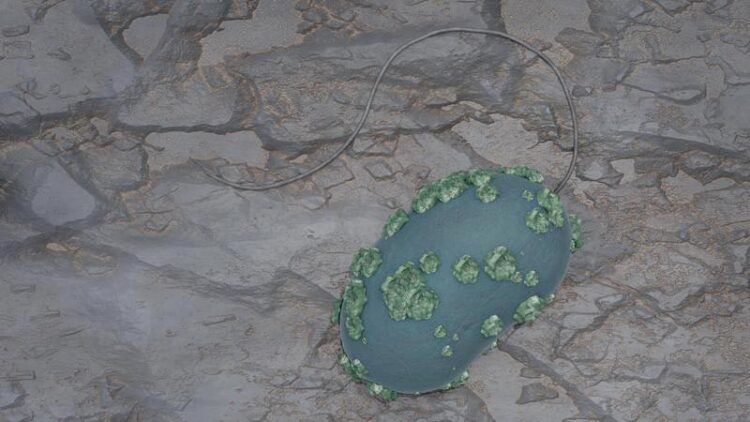
Image of a Desulfosporosinus cell with immobilized uranium on the surface
(c) B. Schröder/ HZDR
Microbial reduction reduces mobility of uranium compounds.
When designing repositories for high-level radioactive waste in deep geological layers, various factors must be carefully considered to ensure their long-term safety. Among other things, natural communities of microorganisms can influence the behavior of the waste, especially when it comes into contact with water. The microorganisms interact with released radionuclides and influence their mobility. Researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have taken a closer look at a microorganism that occurs in the vicinity of a potential repository.
In Germany, rocks that are suitable for the permanently safe storage of highly radioactive waste in a repository – so-called host rocks – are certain clay rock formations in addition to rock salt and crystalline rock. A multi-barrier system is preferred, consisting of the waste container as a technical barrier, the backfill material as a geotechnical barrier and the host rock as a geological barrier. This system is intended to isolate the radioactive waste from the environment.
“The combination of clay formations with the backfill material bentonite, which consists of various clay minerals, is an example of such a system. We know that so-called sulphate-reducing microorganisms occur in both the host rock and in the backfill material. In our work, we investigated a representative of the genus Desulfosporosinus in more detail. We were particularly interested in its influence on uranium present in the bentonite-clay system,” explains Dr. Stephan Hilpmann from the HZDR Institute of Resource Ecology.
Uranium can occur in a variety of compounds and can assume different oxidation states. In natural deposits, uranium is mainly found in tetravalent and hexavalent form. Under normal conditions, tetravalent uranium compounds – in contrast to hexavalent compounds – are almost insoluble in water. Uranium compounds are toxic, whereby the toxicity depends mainly on their solubility. This distinct behavior of the compounds with different oxidation states is of great importance for understanding the processes in the repository.
Microbial defense removes uranium from water
Desulfosporosinus lives under anaerobic conditions: it only grows in the absence of air. This allowed the researchers to study the microorganism under realistic conditions, such as those found in deep layers of rock. To do this, they brought the bacterial cultures into contact with uranium salt solutions in natural pore water of the clay rock, covered by a nitrogen atmosphere that protects them from atmospheric oxygen. They observed that the bacteria convert the easily water-soluble hexavalent uranium into sparingly soluble tetravalent uranium. The bacteria can deposit this sparingly soluble uranium in membrane vesicles on their cell surface in the form of incrustations. The team assumes that this is a defensive reaction of the microorganisms – a behavior that has previously been observed in other types of bacteria. “After one week, the bacteria have converted about 40 percent of the originally dissolved uranium into the poorly soluble variant,” Hilpmann reports.
The team also observed a further oxidation stage with pentavalent uranium, about whose formation in this process not much was previously known. This is mainly due to its typical instability. The researchers suspect that they were only able to detect pentavalent uranium because the bacteria stabilize it to some extent in solution. They were able to detect this oxidation state even after one week.
Multispectral view into contaminated subsurface
To observe the various uranium compounds, the team used a range of modern spectroscopy and microscopy methods. The HZDR researchers have access to highly specialized techniques at the Institute of Ion Beam Physics and Materials Research and at the Rossendorf Beamline (ROBL), which the HZDR operates at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble. At the French site, for example, they can investigate radiochemical processes spectroscopically. Here they have also observed the formation of pentavalent uranium in the process using a method called HERFD-XANES.
HERFD-XANES stands for fluorescence detection with high-energy resolution, which is coupled with X-ray near-edge absorption spectroscopy. This is an X-ray absorption spectroscopic method that can be used to study the behavior of electrons. The team was able to visualize the uranium-containing aggregates on the cell surface of Desulfosporosinus using scanning transmission electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.
“Our findings deepen our understanding of the complex processes in a potential final repository. They may also be relevant for the removal of radioactive pollutants from contaminated waters and thus for their remediation,” says Hilpmann, summarizing the significance of the results.
The work was carried out as part of the “iCross” project, which is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (funding code 02NUK053E) and the Helmholtz Association (funding code SO-093).
Publications:
S. Hilpmann, A. Rossberg, R. Steudtner, B. Drobot, R. Hübner, F. Bok, D. Prieur, S. Bauters, K.O. Kvashnina, T. Stumpf, A. Cherkouk, Presence of uranium(V) during uranium(VI) reduction by Desulfosporosinus hippei DSM 8344T, in Science of The Total Environment, 2023 (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162593 )
X-ray absorption spectroscopy reveals the transient oxidation state during microbial uranium(VI) reduction by a sulfate-reducing microorganism, ESRF Highlights 2023, Ed.: A. Joly, 2024, (https://www.esrf.fr/home/UsersAndScience/Publications/Highlights/esrf-highlights…)
More information:
Dr. Stephan Hilpmann | Dr. Andrea Cherkouk
Institute of Resource Ecology at HZDR
Phone: +49 351 260 2860 | +49 351 260 2989
Email: s.hilpmann@hzdr.de | a.cherkouk@hzdr.de
Media contact:
Simon Schmitt | Head
Department of Communication and Media Relations at HZDR
Phone: +49 351 260 3400 | Mob.: +49 175 874 2865 | Email: s.schmitt@hzdr.de
The Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) performs – as an independent German research center – research in the fields of energy, health, and matter. We focus on answering the following questions:
• How can energy and resources be utilized in an efficient, safe, and sustainable way?
• How can malignant tumors be more precisely visualized, characterized, and more effectively treated?
• How do matter and materials behave under the influence of strong fields and in smallest dimensions?
To help answer these research questions, HZDR operates large-scale facilities, which are also used by visiting researchers: the Ion Beam Center, the Dresden High Magnetic Field Laboratory and the ELBE Center for High-Power Radiation Sources.
HZDR is a member of the Helmholtz Association and has six sites (Dresden, Freiberg, Görlitz, Grenoble, Leipzig, Schenefeld near Hamburg) with almost 1,500 members of staff, of whom about 670 are scientists, including 220 Ph.D. candidates.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Stephan Hilpmann | Dr. Andrea Cherkouk
Institute of Resource Ecology at HZDR
Phone: +49 351 260 2860 | +49 351 260 2989
Email: s.hilpmann@hzdr.de | a.cherkouk@hzdr.de
Originalpublikation:
S. Hilpmann, A. Rossberg, R. Steudtner, B. Drobot, R. Hübner, F. Bok, D. Prieur, S. Bauters, K.O. Kvashnina, T. Stumpf, A. Cherkouk, Presence of uranium(V) during uranium(VI) reduction by Desulfosporosinus hippei DSM 8344T, in Science of The Total Environment, 2023 (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162593 )
X-ray absorption spectroscopy reveals the transient oxidation state during microbial uranium(VI) reduction by a sulfate-reducing microorganism, ESRF Highlights 2023, Ed.: A. Joly, 2024, (https://www.esrf.fr/home/UsersAndScience/Publications/Highlights/esrf-highlights…)
Weitere Informationen:
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…




















