Understanding cellular functions
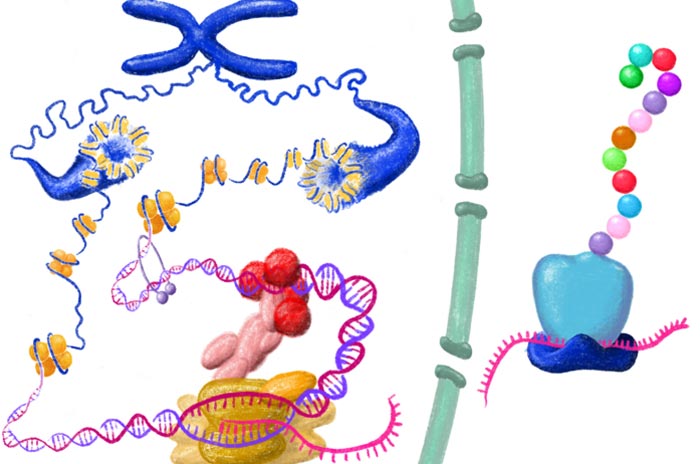
Biopolymers are responsible for regulating processes that are essential to life.
Credit: ill./©: Nike Heinß / CRC 1551
New Collaborative Research Center combines life sciences and polymer research.
German Research Foundation has approved new CRC 1551 “Polymer Concepts in Cellular Function” under the aegis of Mainz University.
The researchers of the new Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1551, funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), intend to apply findings of polymer research to molecular processes in order to better understand what happens in body cells. The CRC entitled “Polymer Concepts in Cellular Function” will be initiated in January 2023 under the lead management of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), jointly with the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB) and the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, both located on the JGU campus, as well as the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt and the University of Stuttgart as strong partners. The participating researchers will focus on the polymer structures of DNA, RNA, and proteins and how the polymer properties of these biomolecules influence their functioning in cells. The DFG has agreed to provide about EUR 9.5 million to fund the work of the new CRC during its first four-year funding period.
Focusing on polymer properties of DNA, RNA, and proteins
Polymers are molecules made up of many, often identical building blocks, such as in plastics. Polymers are molecules made up of many, often identical building blocks, such as in plastics. Essential biological macromolecules, such as DNA, RNA and proteins, are also polymers (biopolymers). “We intend to study the polymer properties of DNA, RNA, and proteins in order to understand how they interact on the biological level,” explained Professor Edward Lemke, the spokesperson of the new CRC. “For this purpose, we have put together outstanding teams of researchers from the fields of the life sciences and polymer research.” They will be facing considerable challenges, since up to 20 percent of the dry mass of each human cell consists of RNA, while DNA, which has a length of two meters, is packed tightly within a cell nucleus with a diameter of just 10 microns – and yet can be transcribed and replicated.
Filling the gap in understanding biopolymer functioning in cells
The polymeric nature of these macromolecules in connection with biological mechanisms has to date received insufficient attention, although it has become apparent in recent years how important knowledge of polymers is for a comprehensive understanding of cellular processes. At the same time, there are marked differences between what can be considered standard polymers and biopolymers. Thus, it is necessary to translate the concepts of polymer research into the field of biology.
“The exchange of knowledge and expertise in our network will not primarily serve to make the techniques of polymer research available to the life sciences,” added Professor Dorothee Dormann, deputy spokesperson of the new CRC and Professor of Molecular Cell Biology at JGU. “One of our long-term aims is to describe and understand the nonequilibrium processes in cells triggered by the complex interplay of numerous cellular polymers.” This research will also help the researchers to better understand how cells age on the molecular level and should provide a basis for the development of a new generation of therapeutics.
Related links:
https://www.grc.uni-mainz.de/prof-edward-a-lemke/ – GRC fellow Professor Edward A. Lemke ;
https://www.imb.de/research/lemke/research/ – Synthetic Biophysics of Protein Disorder group at the IMB ;
https://www.grc.uni-mainz.de/prof-dorothee-dormann/ – GRC fellow Professor Dorothee Dormann ;
https://www.imb.de/research/our-research-groups/dormann/research – Molecular Mechanisms of RNA-binding Protein Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases group at the IMB;
https://www.imb.de/ – Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB) ;
https://www.mpip-mainz.mpg.de/en/home – Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…




















