Substitute for rare earth metal oxides
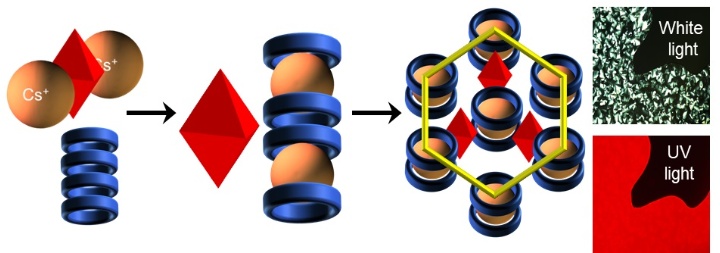
Embedding phosphorescent caesium metal clusters (red octahedrons) in organic liquid crystals (blue rings) produces hybrid nanomaterials that emit intense red light when irradiated with UV light. Photo: University of Stuttgart/ IOC
Nowadays energy conversion in lighting and optoelectronic devices requires the use of rare earth oxides.
However, due to their limited availability from natural resources located outside Europe rare earth oxides are considered as strategic minerals.
Therefore, alternative materials are highly desirable for energy efficient lighting and other applications.
Starting in January 2019 the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) will be funding the Franco-German joint project SNAPSTER (Supramolecular nanomaterials containing phosphorescent transition metal clusters), which involves three research teams from the University of Stuttgart and the University of Rennes.
The aim of the SNAPSTER project is the integration of inorganic, phosphorescent metal clusters in organic liquid crystals via supramolecular interactions.
The liquid crystals are acting as isolating shell and improve the photophysical properties of the resulting hybrid materials and their chemical stability.
The emission wavelengths can be tailored by suitable choice of the metal cluster. SNAPSTER is based on the longstanding complementary expertise of the collaborating teams regarding organic material synthesis and characterization (Sabine Laschat, Stuttgart), inorganic cluster synthesis, photophysical characterization and preparation of hybrid materials (Yann Molard, Rennes) and the integration of these novel materials into electronic devices (Emmanuel Jacques, Rennes).
Sabine Laschat, Institut für Organische Chemie, Universität Stuttgart,
sabine.laschat@oc.uni-stuttgart.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















