Stressed plants must have iron under control
Plants have to absorb a large number of nutrients, but often their availability varies. Then they respond by activating different genetic programs, especially in the case of iron. HHU / Rumen Ivanov
Unlike animals, plants cannot move and tap into new resources when there is a scarcity or lack of nutrients. Instead, they have to adapt to the given situation. They do so by activating sets of stress-specific genes As a result, they basically reprogram their metabolism.
Plant researchers Dr. Tzvetina Brumbarova and PD Dr. Rumen Ivanov from the HHU Institute of Botany (head: Prof. Dr. Petra Bauer) looked at the stress programmes activated by the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
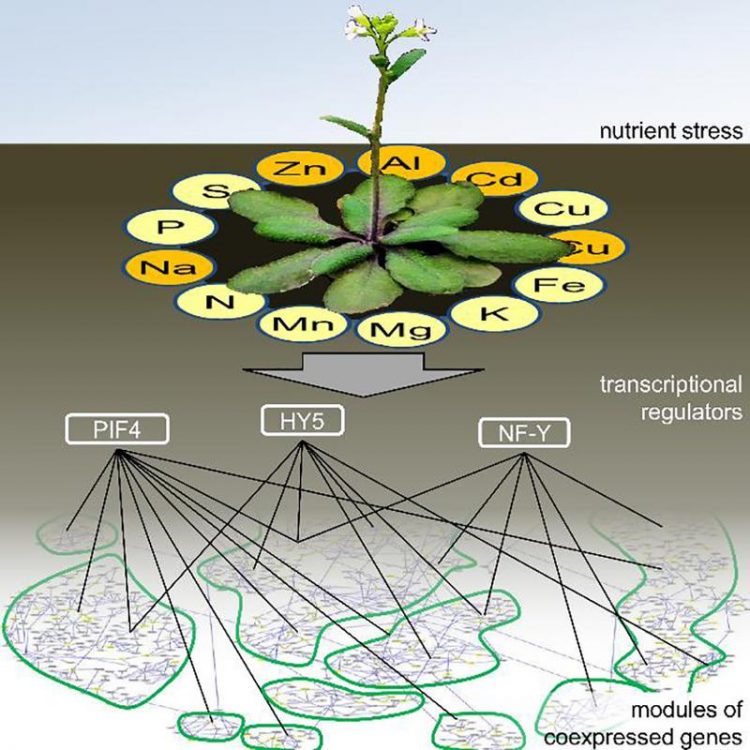
They wanted to find out which response strategies are used by the plant, which is also known as ‘thale cress’. Brumbarova and Ivanov used a computer-assisted approach to analyse extensive gene expression data from the scientific community.
Based on the analysis, the HHU researchers found that the data contained some surprising strategies used by Arabidopsis. Firstly, three of the main regulators identified by the authors to play a role in stress responses are already known: They also control the plant’s response to light.
“This suggests that light can also control nutrient uptake in the subterranean parts of the plant like the roots,” explains Tzvetina Brumbarova.
Even more important is the discovery that plants adapt their iron levels in particular when there is a lack of nutrient availability. Rumen Ivanov says: “In stress situations like these, iron can quickly turn from friend to foe. On the one hand, iron is vital for various processes in order for the plant to survive. On the other hand, however, iron can also result in reactive compounds that can cause irreversible damage to the plant when there is a scarcity of nutrients.”
Yet another discovery took the researchers by surprise. “In the case of stress, the plant mainly tries to adapt iron import within the cell rather than internal iron redistribution,” explains Brumbarova, and goes on to say: “From a cellular perspective, this means that controlling the ‘external borders’ matters most.”
The study, which has now been published online in the journal iScience, is based entirely on available knowledge. Ivanov says: “All the primary data was already available. We simply examined it from a new angle to answer different questions.” As a result, the biologists already have a large dataset that can be used to generate new findings.
Tzvetina Brumbarova and Rumen Ivanov, The Nutrient Response Transcriptional Regulome of Arabidopsis, iScience (2019).
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.07.045
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S258900421930272X?via%3Dihub
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.hhu.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…




















