Rutgers scientists discover 'Legos of life'
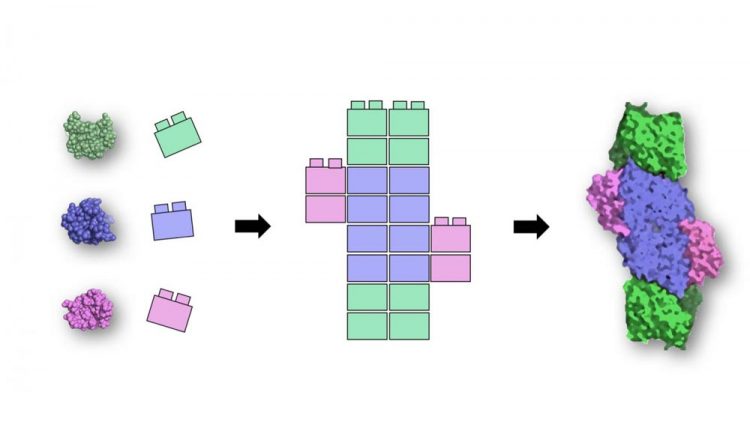
Rutgers researchers identified a small set of simple protein building blocks (left) that likely existed at the earliest stages of life's history. Over billions of years, these 'Legos of life' were assembled and repurposed by evolution into complex proteins (right) that are at the core of modern metabolism. Credit: Vikas Nanda/Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
Rutgers scientists have found the “Legos of life” – four core chemical structures that can be stacked together to build the myriad proteins inside every organism – after smashing and dissecting nearly 10,000 proteins to understand their component parts.
The four building blocks make energy available for humans and all other living organisms, according to a study published online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study's findings could lead to applications of these stackable, organic building blocks for biomedical engineering and therapeutic proteins and the development of safer, more efficient industrial and energy catalysts – proteins and enzymes that, like tireless robots, can repeatedly carry out chemical reactions and transfer energy to perform tasks.
“Understanding these parts and how they are connected to each other within the existing proteins could help us understand how to design new catalysts that could potentially split water, fix nitrogen or do other things that are really important for society,” said Paul G. Falkowski, study co-author and a distinguished professor who leads the Environmental Biophysics and Molecular Ecology Laboratory at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
The scientists' research was done on computers, using data on the 3D atomic structures of 9,500 proteins in the RCSB Protein Data Bank based at Rutgers, a rich source of information about how proteins work and evolve.
“We don't have a fossil record of what proteins looked like 4 billion years ago, so we have to take what we have today and start walking backwards, trying to imagine what these proteins looked like,” said Vikas Nanda, senior author of the study and an associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Rutgers' Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, within Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences. “The study is the first time we've been able to take something with thousands of amino acids and break it down into reasonable chunks that could have had primordial origins.”
The identification of four fundamental building blocks for all proteins is just a beginning. Nanda said future research may discover five or 10 more building blocks that serve as biological Legos.
“Now we need to understand how to put these parts together to make more interesting functional molecules,” he said. “That's the next grand challenge.”
###
The study's lead author is Hagai Raanana, a post-doctoral associate in the Environmental Biophysics and Molecular Ecology Program. Co-authors include Douglas H. Pike, a doctoral student at the Rutgers Institute for Quantitative Biomedicine, and Eli K. Moore, a post-doctoral associate in the Environmental Biophysics and Molecular Ecology Program.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions…

An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of a powerful epigenetic editing technology, which unlocks the ability to precisely program chromatin modifications. Understanding how…

NASA selects UF mission to better track the Earth’s water and ice
NASA has selected a team of University of Florida aerospace engineers to pursue a groundbreaking $12 million mission aimed at improving the way we track changes in Earth’s structures, such…