Earliest life or rare dirt?
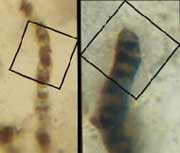
Life forms: Schopf thinks these marks are fossils of ancient bacteria. <br>© Nature <br>
Gloves are coming off in ancient bacteria bust-up.
A claim to have found evidence of the oldest living things on Earth is being fiercely contested. The argument looks set to run and run, and no one may win, but it may lead to a better understanding of the origins of life on our planet.
The debate is academic, but its implications are not. The ’fossil bacteria’ in question are around 3.5 billion years old. That’s roughly one billion years older than the only confirmed fossil bacteria.
This would mean that complex biochemistry – including photosynthesis – originated around one billion years after the Earth formed. Photosynthesis released oxygen into the atmosphere, which has supported the majority of life ever since.
Dark microscopic squiggles in rocks called ’Apex chert’ from Western Australia, are the fossils of various species of cyanobacteria, according to William Schopf of the University of California, Los Angeles1.
A team led by Martin Brasier at the University of Oxford, UK, believes that Schopf’s ’fossils’, although unusual, are simply tiny clumps of impurities in the rock2.
Fellow researchers are loath to be named for fear of “exacerbating what looks like becoming an acrimonious debate”, according to one. They are nonetheless following the details closely. “This is a fascinating debate,” says another.
Most agree that the age of the Apex chert rocks may preclude either side ever being proved right.
Technical point
Schopf’s team studied the structure and chemical composition of the squiggles with a technique called laser-Raman imagery. The group argues that the marks are made up of carbon molecules, which are the decay products of living bacterial cells. “They are tiny little fossils,” says Schopf.
Brasier’s team repeated some of Schopf’s analyses recently and disagrees. “Schopf’s hypothesis is deeply flawed,” Brasier says.
Brasier’s team agrees that the marks’ chemical composition appears biological in origin. But the group thinks that they actually arose through unusual geological processes around ancient hydrothermal vents, where hot volcanic gases rise to the surface.
What’s more, the group says, the squiggles look nothing like other ancient microbes. “The shapes are far too complicated to be bacteria,” says Brasier, who feels Schopf should drop his claim.
Brasier’s group asserts that biological-seeming molecules can result from reactions between the carbon dioxide and monoxide released by hot, metal-rich hydrothermal vents. These molecules could then have been sculpted into bacteria-esque filaments as the hot rocks they were born in cooled.
If this was the case, argues Schopf, such material would be found everywhere. So far it hasn’t been. “The facts are going to win and I’ve got the data,” he says.
Win-win?
The one thing both parties agree on is that only time will tell. Schopf is continuing to analyse his putative fossils. A nanoscale examination of their ’cell membranes’ will, he claims, prove beyond doubt that the Apex chert does contain the oldest known remains of life on Earth.
Brasier and his team are now investigating the kind of chemical reactions that they believe produced the squiggles. The researchers suspect the reactions could themselves have created complex molecules such as amino acids and be the source of life on Earth. “Schopf may have stumbled on a site that may explain how life got started,” says Brasier.
References
- Schopf, J. W., Kudryavtsev, A. B., Agresti, D. G., Wdowiak, T. J. & Czaja, A. D. Laser-Raman imagery of Earth’s earliest fossils. Nature, 416, 73 – 76, (2002).
- Brasier, D. M. et al. Questioning the evidence for Earth’s oldest fossils. Nature, 416, 76 – 81, (2002).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Faster, more energy-efficient way to manufacture an industrially important chemical
Zirconium combined with silicon nitride enhances the conversion of propane — present in natural gas — needed to create in-demand plastic, polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common type of plastic found…

Energy planning in Ghana as a role model for the world
Improving the resilience of energy systems in the Global South. What criteria should we use to better plan for resilient energy systems? How do socio-economic, technical and climate change related…

Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes
Artificial blood vessels could improve heart bypass outcomes. 3D-printed blood vessels, which closely mimic the properties of human veins, could transform the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Strong, flexible, gel-like tubes…




















