From Nose to Knee: Engineered Cartilage Regenerates Joints
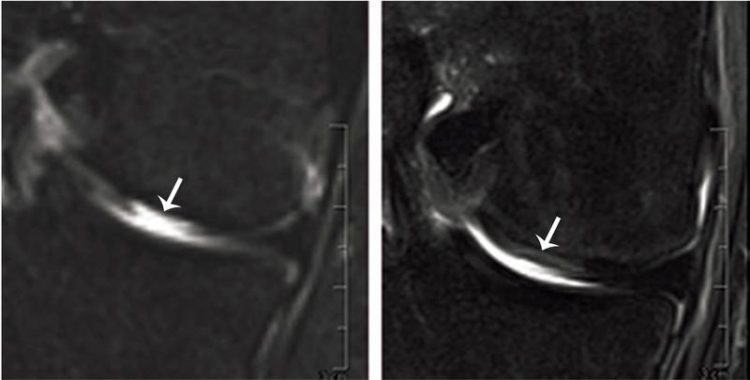
Articular cartilage replaced: MRI of defect tissue site before (left) and four months after (right) transplantation. Fig: Department of Biomedicine, University of Basel
The nasal cartilage cells' ability to self-renew and adapt to the joint environment is associated with the expression of so-called HOX genes. The scientific journal Science Translational Medicine has published the research results together with the report of the first treated patients.
Cartilage lesions in joints often appear in older people as a result of degenerative processes. However, they also regularly affect younger people after injuries and accidents. Such defects are difficult to repair and often require complicated surgery and long rehabilitation times.
A new treatment option has now been presented by a research team lead by Prof. Ivan Martin, professor for tissue engineering, and Prof. Marcel Jakob, Head of Traumatology, from the Department of Biomedicine at the University and the University Hospital of Basel: Nasal cartilage cells can replace cartilage cells in joints.
Cartilage cells from the nasal septum (nasal chondrocytes) have a distinct capacity to generate a new cartilage tissue after their expansion in culture. In an ongoing clinical study, the researchers have so far taken small biopsies (6 millimeters in diameter) from the nasal septum from seven out of 25 patients below the age of 55 years and then isolated the cartilage cells.
They cultured and multiplied the cells and then applied them to a scaffold in order to engineer a cartilage graft the size of 30 x 40 millimeters. A few weeks later they removed the damaged cartilage tissue of the patients' knees and replaced it with the engineered and tailored tissue from the nose. In a previous clinical study conducted in cooperation with plastic surgeons and using the same method, the researchers from Basel recently already successfully reconstructed nasal wings affected by tumors.
Surprising Adaption
The scientists around first author Dr. Karoliina Pelttari were especially surprised by the fact that in the animal model with goats, the implanted nasal cartilage cells were compatible with the knee joint profile; even though, the two cell types have different origins.
During the embryonic development, nasal septum cells develop from the neuroectodermal germ layer, which also forms the nervous system; their self-renewal capacity is attributed to their lack of expression of some homeobox (HOX) genes. In contrast, these HOX genes are expressed in articular cartilage cells that are formed in the mesodermal germ layer of the embryo.
“The findings from the basic research and the preclinical studies on the properties of nasal cartilage cells and the resulting engineered transplants have opened up the possibility to investigate an innovative clinical treatment of cartilage damage”, says Prof. Ivan Martin about the results.
It has already previously been shown that the human nasal cells' capacity to grow and form new cartilage is conserved with age. Meaning, that also older people could benefit from this new method, as well as patients with large cartilage defects. While the primary target of the ongoing clinical study at the University Hospital of Basel is to confirm the safety and feasibility of cartilage grafts engineered from nasal cells when transplanted into joint, the clinical effectiveness assessed until now is highly promising.
Original source
Karoliina Pelttari, Benjamin Pippenger, Marcus Mumme, Sandra Feliciano, Celeste Scotti, Pierre Mainil-Varlet, Alfredo Procino, Brigitte von Rechenberg, Thomas Schwamborn, Marcel Jakob, Clemente Cillo, Andrea Barbero, Ivan Martin
Adult human neural crest-derived cells for articular cartilage repair
Science Translational Medicine, 6, 251ra120 (2014) | doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009688
Further information
Prof. Dr. Ivan Martin, Department of Biomedicine at the University and the University Hospital of Basel, phone: +41 (0)61 265 23 84, email: ivan.martin@unibas.ch
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















