Beyond Elastic: Organic crystal demonstrates superelasticity
Superelasticity, also called “pseudoelasticity”, is the ability of special materials that have undergone extensive deformation to return to their original shape when the pressure is released.
This allows some alloys to be stretched out about ten times more than common spring steel without being permanently deformed. The mechanism is different from that involved in the normal elasticity of rubbery substances. In rubber, the polymer chains are stretched out through strain—no compression is possible.
In superelastic materials, mechanical stress triggers a change in the crystal structure—without the individual atoms changing places. When the stress is removed, the materials return to their former structure. Such substances are interesting candidates for use as building materials with “shape memory” in applications such as “self-repairing” vehicle parts.
Superelastic materials other than metal alloys and ceramics have not appeared for over 80 years since the first report of superelasticity in metal alloys. This phenomenon was previously unknown in organic materials. Satoshi Takamizawa of Yokohama City University has now found superelasticity in an organic crystal for the first time: terepthalamide crystals exhibit superelastic behavior with surprisingly little application of force.
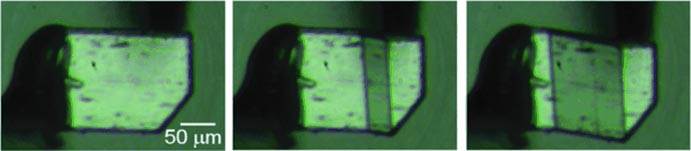
Shear stress on a specific surface of the crystal initially causes the crystal to bend, and then transition to a different crystal phase. The more pressure that is applied, the more this spreads throughout the crystal.
When the tension is released, the phase transition moves back across the crystal, which returns to its original structure. Takamizawa and one of his students were able to repeat this superelastic deformation 100 times without any signs of material fatigue.
The crystal consists of individual sheets of slanted terepthalamide molecules (AAAAA sheet arrangement). Shear stress causes the angles of the molecules within the layers to change, which results in a more densely packed A’BA’BA’B sheet arrangement. The layers are held together by a network of hydrogen bridge bonds, which break under pressure and rearrange during the phase transition.
Possible applications of organic superelastic materials include joints made of a single component and elements for dampening vibrations. In medicine, implants made from these types of materials could be deformed for easy introduction and then return to the desired shape and size when they reach the desired location.
About the Author
Dr. Satoshi Takamizawa is Professor of Inorganic Chemistry at Yokohama City University. His main interest is crystal function in coordination compounds and related organic and inorganic materials.
Author: Satoshi Takamizawa, Yokohama City University (Japan), http://nanochem.sci.yokohama-cu.ac.jp/
Title: A Superelastic Crystal of Terephthalamide
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Permalink to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201311014
Media Contact
More Information:
http://pressroom.angewandte.orgAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















