'Swiss cheese' design enables thin film silicon solar cells with potential for higher efficiencies
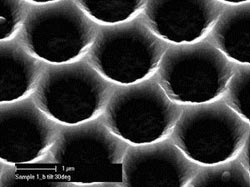
This SEM micrograph shows the nanostructured ZnO layer, Swiss cheese design for Micromorph solar cells. Credit: Milan Vanecek, Institute of Physics, Prague<br>
One long-term option for low-cost, high-yield industrial production of solar panels from abundant raw materials can be found in amorphous silicon solar cells and microcrystalline silicon tandem cells (a.k.a. Micromorph)—providing an energy payback within a year.
A drawback to these cells, however, is that the stable panel efficiency is less than the efficiency of presently dominate crystalline wafer-based silicon, explains Milan Vanecek, who heads the photovoltaic group at the Institute of Physics in Prague.
“To make amorphous and microcrystalline silicon cells more stable they're required to be very thin because of tight spacing between electrical contacts, and the resulting optical absorption isn't sufficient,” he notes. “They're basically planar devices. Amorphous silicon has a thickness of 200 to 300 nanometers, while microcrystalline silicon is thicker than 1 micrometer.”
The team's new design focuses on optically thick cells that are strongly absorbing, while the distance between the electrodes remains very tight. They describe their design in the American Institute of Physics' journal Applied Physics Letters.
“Our new 3D design of solar cells relies on the mature, robust absorber deposition technology of plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, which is a technology already used for amorphous silicon-based electronics produced for liquid crystal displays. We just added a new nanostructured substrate for the deposition of the solar cell,” Vanecek says.
This nanostructured substrate consists of an array of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocolumns or, alternatively, from a “Swiss cheese” honeycomb array of micro-holes or nano-holes etched into the transparent conductive oxide layer (ZnO) (See Figure).
“This latter approach proved successful for solar cell deposition,” Vanecek elaborates. “The potential of these efficiencies is estimated within the range of present multicrystalline wafer solar cells, which dominate solar cell industrial production. And the significantly lower cost of Micromorph panels, with the same panel efficiency as multicrystalline silicon panels (12 to 16 percent), could boost its industrial-scale production.”
The next step is a further optimization to continue improving efficiency.
The article, “Nanostructured 3-dimensional thin film silicon solar cells with very high efficiency potential,” by Milan Vanecek, Oleg Babchenko, Adam Purkrt, Jakub Holovsky, Neda Neykova, Ales Poruba, Zdenek Remes, Johannes Meier, and Ulrich Kroll, appears in the journal Applied Physics Letters.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.aip.orgAll latest news from the category: Interdisciplinary Research
News and developments from the field of interdisciplinary research.
Among other topics, you can find stimulating reports and articles related to microsystems, emotions research, futures research and stratospheric research.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…