Researchers develop new AI system using light to learn associatively
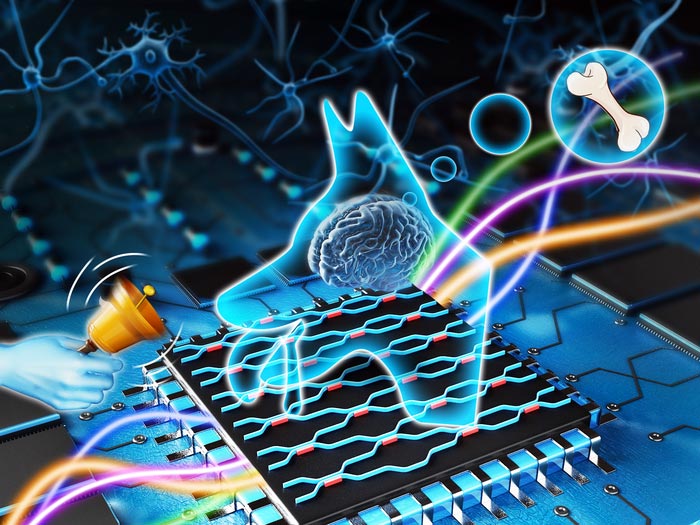
An illustration of Pavlov's experiment on associated learning and a computer chip
Credit: Zengguang Cheng
Seeing the light:
Researchers at Oxford University’s Department of Materials, working in collaboration with colleagues from Exeter and Munster have developed an on-chip optical processor capable of detecting similarities in datasets up to 1,000 times faster than conventional machine learning algorithms running on electronic processors.
The new research published in Optica took its inspiration from Nobel Prize laureate Ivan Pavlov’s discovery of classical conditioning. In his experiments, Pavlov found that by providing another stimulus during feeding, such as the sound of a bell or metronome, his dogs began to link the two experiences and would salivate at the sound alone. The repeated associations of two unrelated events paired together could produce a learned response – a conditional reflex.
Co-first author Dr James Tan You Sian, who did this work as part of his DPhil in the Department of Materials, University of Oxford said: ‘Pavlovian associative learning is regarded as a basic form of learning that shapes the behaviour of humans and animals – but adoption in AI systems is largely unheard of. Our research on Pavlovian learning in tandem with optical parallel processing demonstrates the exciting potential for a variety of AI tasks.’
The neural networks used in most AI systems often require a substantial number of data examples during a learning process – training a model to reliably recognise a cat could use up to 10,000 cat/non-cat images – at a computational and processing cost.
Rather than relying on backpropagation favoured by neural networks to ‘fine-tune’ results, the Associative Monadic Learning Element (AMLE) uses a memory material that learns patterns to associate together similar features in datasets – mimicking the conditional reflex observed by Pavlov in the case of a ‘match’.
The AMLE inputs are paired with the correct outputs to supervise the learning process, and the memory material can be reset using light signals. In testing, the AMLE could correctly identify cat/non-cat images after being trained with just five pairs of images.
The considerable performance capabilities of the new optical chip over a conventional electronic chip are down to two key differences in design:
- a unique network architecture incorporating associative learning as a building block rather than using neurons and a neural network
- the use of ‘wavelength-division multiplexing’ to send multiple optical signals on different wavelengths on a single channel to increase computational speed.
The chip hardware uses light to send and retrieve data to maximise information density – several signals on different wavelengths are sent simultaneously for parallel processing which increases the detection speed of recognition tasks. Each wavelength increases the computational speed.
Professor Wolfram Pernice, co-author from Münster University explained: ‘The device naturally captures similarities in datasets while doing so in parallel using light to increase the overall computation speed – which can far exceed the capabilities of conventional electronic chips.’
An associative learning approach could complement neural networks rather than replace them clarified co-first author Professor Zengguang Cheng, now at Fudan University.
‘It is more efficient for problems that don’t need substantial analysis of highly complex features in the datasets’ said Professor Cheng. ‘Many learning tasks are volume based and don’t have that level of complexity – in these cases, associative learning can complete the tasks more quickly and at a lower computational cost.’
‘It is increasingly evident that AI will be at the centre of many innovations we will witness in the coming phase of human history. This work paves the way towards realising fast optical processors that capture data associations for particular types of AI computations, although there are still many exciting challenges ahead.’ said Professor Harish Bhaskaran, who led the study.
The full paper, ‘Monadic Pavlovian associative learning in a backpropagation-free photonic network,’ is available in the journal Optica.
Journal: Optica
DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.455864
Method of Research: Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Monadic Pavlovian associative learning in a backpropagation-free photonic network
Article Publication Date: 13-Jul-2022
Media Contact
Clea Boorman
University of Oxford
clea.boorman@tss.ox.ac.uk
Office: +44 (0)1865 280528
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…