SMART-1 detects calcium on the Moon
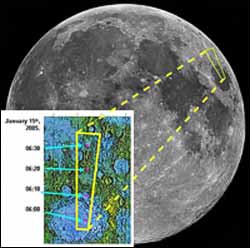
Calcium in Mare Crisium
Thanks to measurements by the D-CIXS X-ray spectrometer, ESA’s SMART-1 spacecraft has made the first ever unambiguous remote-sensing detection of calcium on the Moon.
SMART-1 is currently performing the verification and calibration of its instruments, while it runs along its science orbit, reaching 450 kilometres from the Moon at its closest distance. During this calibration phase, which precedes the actual science observations phase, the SMART-1 scientists are getting acquainted with the delicate operations and the performance of their instruments in the warm environment of the lunar orbit.
Although it is still preparing for full lunar operations, D-CIXS has started already sending back high-quality data. D-CIXS is designed to measure the global composition of the Moon by observing how it glows in X-rays when the Sun shines on it. In fact, different chemical elements provide their ‘fingerprinting’, each glowing in a unique way.
On 15 January 2005, between 07:00 and about 09:00 Central European Time, a solar flare occurred, blasting a quantity of radiation that flooded the Solar System and the Moon. “The Sun was kind to us”, said Prof Manuel Grande of the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, leader of the D-CIXS instrument team. “It set off a large X-ray flare just as we took our first look downwards at the lunar surface”.
The lunar surface reacts to the incoming solar radiation by glowing in different X-ray wavelengths. This enabled D-CIXS, , to distinguish the presence of chemical elements – including calcium, aluminium, silicon and iron – in Mare Crisium, the area of the lunar surface being observed at that moment. “It is the first time ever that calcium has been unambiguously detected on the Moon by remote-sensing instrumentation”, added Prof. Grande. Calcium is an important rock-forming element on the Moon.
“Even before our scientists have finished setting up the instruments, SMART-1 is already producing brand new lunar science”, said Bernard Foing, SMART-1 Project Scientist. “When we get D-CIXS and the other instruments fully tuned, with scientific data rolling in routinely, we should have a truly ground-breaking mission”.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















