The time is ripe for Salmonella
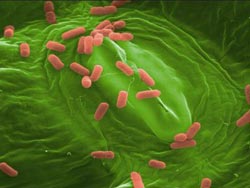
This image shows the association of Escherichia coli with rocket leaves. Credit: Rob Shaw<br>
A wide range of fresh produce has been linked to outbreaks of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica including melons, jalapeño and serrano peppers, basil, lettuce, horseradish sprouts and tomatoes. Researchers at Imperial College London are looking at how these bacterial pathogens latch onto fruits and vegetables and establish themselves in the first place.
They have discovered that strains of Salmonella behave differently when attached to ripe and unripe tomatoes. “Bacteria that attach to ripe tomatoes produce an extensive network of filaments, which is not seen when they attach to the surface of unripe tomatoes. This could affect how they are maintained on the surface,” explained Professor Gad Frankel who is leading the research. “We are not completely sure yet why this happens; it might be due to the surface properties of the tomatoes or alternatively the expression of ripening hormones.”
This is just one example of the subtle interplay between food-poisoning microbes and the fresh produce they contaminate, that determines how pathogens become established in the food chain. “Apart from Salmonella, strains of E. coli are also particularly devious in the way they interact with plant surfaces. They have hair-like appendages and flagella they can use as hooks to successfully secure themselves onto things like salad leaves.”
Although fresh fruits and vegetables are recognized as important vehicles that transmit harmful bacteria, they are still important components of a healthy and balanced diet. “By and large, raw fruits and vegetables are safe to eat and provide numerous health benefits. By working out the reasons behind sporadic outbreaks of infections, we can control these better and help maintain consumer confidence. By improving food safety we would also see important economical and health benefits.”
Understanding how bacteria interact with fresh produce is a crucial but only the first step, explained Professor Frankel. “Translating research into new policies or methods for decontamination is the challenge for future studies,” he said.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.sgm.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















