Predatory organisms at depth
<br>
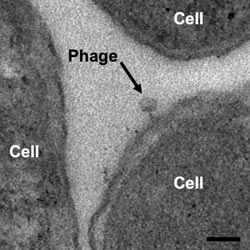
In the current issue of the Journal of the International Society for Microbial Ecology (ISME Journal, 20.1.2014) scientists from the University of Oldenburg and from the GFZ German Centre for Geosciences show that in deep, old and nutrient-poor marine sediments there are up to 225 times more viruses than microbes.
In such extreme habitats viruses make up the largest fraction of living biomass and take over the role as predators in this bizarre ecosystem.
The scientists found that with decreasing nutrient levels the ratio between viruses and cells shifts more toward viruses.
“For several years it has been know that the biomass of all microbes within the sea floor equals that of all life in the oceans above” reports Jens Kallmeyer from the GFZ. “Viruses, however, have been neglected previously”.
In these extreme environments viruses take over the role of predatory organisms: They control size and composition of the microbial community. The surprisingly high number of viruses can be explained by the fact that the small but active microbial community permanently produces new viruses that remain in the sediment for longer times because the few microbes produce fewer enzymes that can destroy viruses.
Previous measurements in seawater and surficial sediments showed that viruses are about ten times more abundant than microbes, but because of their much smaller biomass they did not play a major role in estimates of the total living biomass. Moreover, it was assumed that predators such as unicellular organisms, but also worms and snails control the size of the microbial population. The new results show that these simple assumptions are no longer valid.
Engelhardt, T., Kallmeyer, J., Cypionka, H., & Engelen, B. (2014): „High virus-to-cell ratios indicate ongoing production of viruses in deep subsurface sediments”, ISME Journal. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.245; 20.01.2014
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.gfz-potsdam.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















