Nanotechnology with proteins
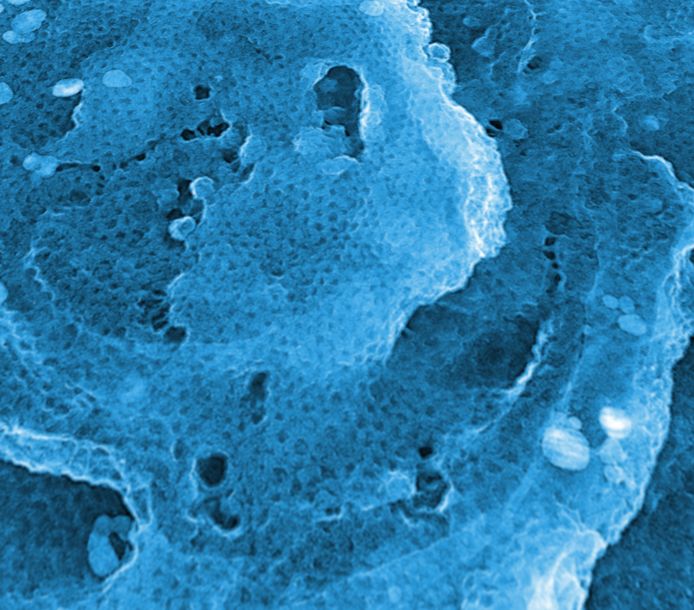
Electron micrograph of a rough aluminium surface coated with a regular clathrin webbing (size is approximately 1.5 x 1.5 micrometers). Foto: Universität Göttingen
For over two decades, scientists have been using DNA to design nanomaterials. Researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Medical School Hanover, both in Germany, have now discovered a new method to use proteins to construct two-dimensional webbings. The results were published in the scientific journal Nature Nanotechnology.
The use of proteins in nanotechnology is a largely unexplored area. “However, due to their complex structure, proteins offer many possibilities to develop novel materials with unique properties,” explains Dr. Iwan A.T. Schaap from Göttingen University’ Third Institute of Physics.
The protein clathrin is normally involved in the formation of transport vesicles inside cells. The scientists show in their study that clathrin can also be used to form two-dimensional webbings on almost any type of surface. “This could revolutionize the design of biological sensors and biosynthetic reactors,” says Dr. Schaap.
After the researchers composed the clathrin-building blocks into a regular hexagonal lattice with a periodicity of only 30 nanometers, they developed a stabilization scheme. “It is essential that the protein structures are robust so that the nanotechnological devices will have a long lifetime and shelf-life,” explains Dr. Schaap.
Finally, the researchers showed how the clathrin webbings can be converted into functional devices by the binding of small metallic particles and active biomolecules.
The researchers will continue their work on these novel protein structures with the aim of developing more efficient nanotechnological devices that can be used for sensing applications and the synthesis of biomolecules.
Original publication: Philip N. Dannhauser et al. Durable protein lattices of clathrin that can be functionalized with nanoparticles and active biomolecules. Nature Nanotechnology 2015. Doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.206.
Contact:
Dr. Iwan A.T. Schaap
Georg-August-Universität Göttingen
Faculty of Physics – III. Physical Institute
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Phone +49 551 39-22816
Email: ischaap@gwdg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















