Cerebrospinal fluid signals control the behavior of stem cells in the brain
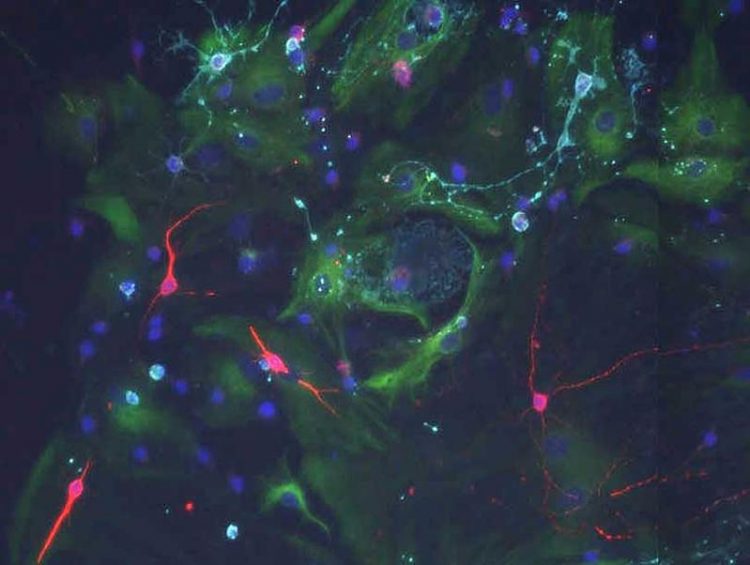
When stem cells from the old brain are cultured with signals of a young choroid plexus they can divide and form new neurons (red). Biozentrum, University of Basel
Stem cells are non-specialized cells found in different organs. They have the capacity to generate specialized cells in the body. In the adult brain, neural stem cells give rise to neurons throughout life. The stem cells reside in unique micro-environments, so-called niches which provide key signals that regulate stem cell self-renewal and differentiation.
Stem cells in the adult brain contact the ventricles, cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that bathes and protects the brain. The CSF is produced by the choroid plexus. The research team led by Prof. Fiona Doetsch at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now shown that the choroid plexus is a key component of the stem cell niche, whose properties change throughout life and affect stem cell behavior.
Choroid plexus signals regulate stem cells
Fiona Doetsch’s group uncovered that the choroid plexus secretes a wide variety of important signaling factors in the CSF, which are important for stem cell regulation throughout life. During aging, the levels of stem cell division and formation of new neurons decrease.
The research team showed that although stem cells are still present in the aged brain, and have the capacity to divide, they do so less. “One reason is that signals in the old choroid plexus are different. As a consequence stem cells receive different messages and are less capable to form new neurons during aging. In other words, compromising the fitness of stem cells in this brain region”, explains Violeta Silva Vargas, the first author of the study.
“But what is really amazing is that when you cultivate old stem cells with signals from young fluid, they can still be stimulated to divide – behaving like the young stem cells”.
A new path to understand brain function in health and disease
In the future, the research team plans to investigate the composition of the signaling factors secreted by the choroid plexus, as well as how these change in different states and affect neural stem cells. This could provide new paths for altering brain function in health and disease. “We can imagine the choroid plexus as a watering can that provides signals to the stem cells. Our investigations also open a new route for understanding how different physiological states of the body influence stem cells in the brain during health and disease, and opens new ways for thinking about therapy”, says Fiona Doetsch.
Original article:
Violeta Silva-Vargas, Angel R. Maldonado-Soto, Dogukan Mizrak, Paolo Codega, Fiona Doetsch: Age-Dependent Niche Signals from the Choroid Plexus Regulate Adult Neural Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell, published online 21 July 2016.
Further Information:
Heike Sacher, University of Basel, Biozentrum, Communications, Tel. +41 61 267 14 49, email: heike.sacher@unibas.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…





















