A Macromolecular Shredder for RNA
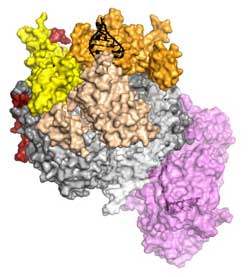
The crystal structure of a complete eukaryotic RNA Exosome complex reveals how it recognizes and processes its substrate. RNA (black) is recognized and unwound by the cap proteins (yellow, beige, orange), threaded inside the barrel (grey) and targeted to the active site of the catalytic subunit (in violet), where processive degradation occurs.<br>Graphics: Debora L. Makino/Copyright: MPI of Biochemistry<br>
Much in the same way as we use shredders to destroy documents that are no longer useful or that contain potentially damaging information, cells use molecular machines to degrade unwanted or defective macromolecules.
Scientists of the MPI of Biochemistry have now decoded the structure and the operating mechanism of the Exosome, a macromolecular machine responsible for degradation of ribonucleic acids (RNAs) in eukaryotes.
One of the functions of RNAs is to permit translation of the genomic information into proteins. The results of the studies now published in Nature show that the structural architecture and the main operation mode of the Exosome are conserved in all domains of life.
Any errors that occur during the synthesis of RNA molecules or unwanted accumulation of RNAs can be damaging to the cell. The elimination of defective RNAs or of RNAs that are no longer needed are therefore key steps in the metabolism of a cell. The Exosome, a multi-protein complex, is a key machine that shreds RNA into pieces. In addition, the Exosome also processes certain RNA molecules into their mature form. However, the molecular mechanism of how the Exosome performs these functions has been elusive.
A ubiquitous molecular shredder
Debora Makino, a postdoctoral researcher in the Research Department led by Elena Conti has now obtained an atomic resolution picture of the complete eukaryotic Exosome complex bound to an RNA molecule. The structure of this complex allowed the scientists to understand how the Exosome works.
“It is quite an elaborate machine: the Exosome complex forms a hollow barrel formed by nine different proteins through which RNA molecules are threaded to reach a tenth protein, the catalytic subunit that then shreds the RNA into pieces,” says Debora Makino. The barrel is essential for this process because it helps to unwind the RNA and prepares it for shredding. “Cells lacking any of the ten proteins do not survive and this shows that not only the catalytic subunit but also the entire barrel is critical for the function of the Exosome,” Makino explains.
The RNA-binding and threading mechanism used by the Exosome in eukaryotes is very similar to that of the Exosome in bacteria and archaebacteria that the researchers had structurally characterized in earlier studies. “Although the chemistry of the shredding reaction in eukaryotes is very different from that used in bacteria and archaebacteria, the channeling mechanism of the Exosome is conserved, and conceptually similar to the channeling mechanism used by the Proteasome, a complex for shredding proteins,” says Elena Conti.
In the future, the researchers want to understand how the Exosome is selectively targeted by the RNAs earmarked for degradation and how it is regulated in the different cellular compartments.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















