Making a tiny rainbow
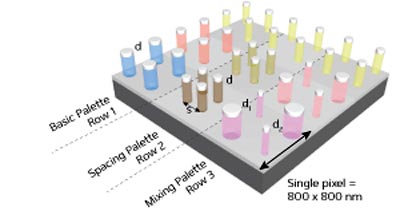
Three strategies for producing colors of pixels containing four aluminum nanodisks. Row 1: varying the nanodisk diameter (d) gives 15 colors. Row 2: Varying both the spacing (s) and diameter (d) of the nanodisks gives over 300 colors. Row 3: Varying the diameters (d1 and d2) of the two pairs of diametrically opposite nanodisks gives over 100 colors. Modified, with permission, from Ref. 1 © 2014 American Chemical Society
A scheme for greatly increasing the number of colors that can be produced by arrays of tiny aluminum nanodisks has been demonstrated by A*STAR scientists1.
Conventional pigments produce colors by selectively absorbing light of different wavelengths — for example, red ink appears red because it absorbs strongly in the blue and green spectral regions. A similar effect can be realized at a much smaller scale by using arrays of metallic nanostructures, since light of certain wavelengths excites collective oscillations of free electrons, known as plasmon resonances, in such structures.
An advantage of using metal nanostructures rather than inks is that it is possible to enhance the resolution of color images by a hundred fold. This enhanced resolution, at the diffraction limit of light, is critical for data storage, digital imaging and security applications. Aluminum — because of its low cost and good stability — is a particularly attractive material to use.
Joel Yang and Shawn Tan at the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering and co-workers used an electron beam to form arrays of approximately 100-nanometer-tall pillars. They then deposited a thin aluminum layer on top of the pillars and in the gaps between them. In these arrays, each pixel was an 800-nanometer-long square containing four aluminum nanodisks.
The plasmon resonance wavelength varies sensitively with the dimensions of the nanostructures. Consequently, by varying the diameter of the four aluminum nanodisks in a pixel (all four nanodisks having the same diameter), the scientists were able to produce about 15 distinct colors — a good start, but hardly enough to faithfully reproduce full-color images.
By allowing two pairs of diametrically opposite nanodisks to have different diameters from each other, then varying the two diameters enabled them to increase this number to over 100. Finally, they generated over 300 colors by varying both the nanodisk diameter (but keeping all four diameters within a pixel the same) and the spacing between adjacent nanodisks in a pixel (see image). “This method is analogous to half-toning used in ink-based printing and results in a broad color gamut,” comments Yang.
The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of their extended palette using a Monet painting. They reproduced the image using both a limited and extended palette, with a much better color reproduction from the extended palette. Amazingly, they shrank the image from 80 centimeters to a mere 300 micrometers — a 2,600-fold reduction in size.
“The use of a more cost-effective metal has the potential to move this technology closer to adoption,” Tan notes.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering. More information about the group’s research can be found at the Plasmonic and Semiconductor Nanostructures Laboratory webpage.
Reference
Tan, S. J., Zhang, L., Zhu, D., Goh, X. M., Wang, Y. M. et al. Plasmonic color palettes for photorealistic printing with aluminum nanostructures. Nano Letters 14, 4023–4029 (2014). | article
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















